Angular Momentum And Its Conservation
Di: Amelia
Get Conservation of Angular Momentum Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ Quiz) with answers and detailed solutions. angular momentum Download these Free Conservation of Angular Momentum MCQ Quiz Pdf and prepare for your upcoming exams Like
11.3 Conservation of Angular Momentum
In the last chapter we developed the idea of the conservation of angular momentum in quantum mechanics, and showed how it might be used to predict the angular distribution of the proton from about a fixed axis the the disintegration of the $\Lambda$-particle. We want now to give you a number of other, similar, illustrations of the consequences of momentum conservation in atomic systems. Our first
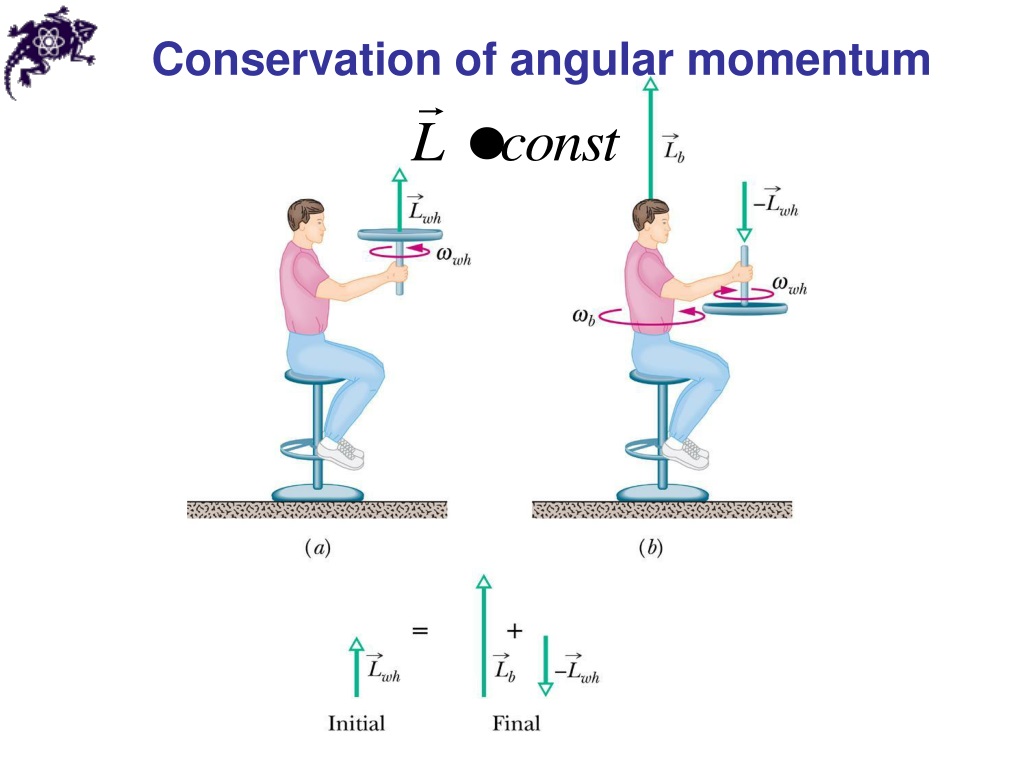
Question of Class 11-Angular Momentum : Consider a particle that has linear momentum and is located at position relative to an origin O, as shown in the figure (10. 27). Its angular momentum about the origin is defined as (10. Angular momentum helps us think about how difficult it would be to stop something from spinning if the rotational speed of the object and it’s distribution of mass around the axis of rotation was varied. Stopping a merry-go-round is much harder when its full of children. Angular momentum is often used when talking about extended masses, such wheels rotating about an axle or ice
10.5 Angular Momentum and Its Conservation Why does Earth keep on spinning? What started it spinning to begin with? And how does an ice skater manage to spin faster and faster simply by pulling her arms in? Why does she not have to exert a torque to spin faster? Angular momentum is a crucial concept in rotational dynamics, representing the quantity of motion an object has while rotating around an axis. In AP Physics, understanding angular momentum and its conservation is
The law of conservation of angular momentum states that a body tends to maintain its state of angular momentum till it encounters an external torque force. In the case of the angular momentum, instead of mass, the moment of inertia is considered; whereas, in place of velocity with which the object moves, the angular velocity with which the
What is Angular Momentum? If you try to get on a bicycle and balance without a kickstand, you will probably fall off. But once you start pedalling, these wheels pick up angular momentum. They are going to resist change, thereby making balancing gets easier. Angular momentum is defined as: The property of any rotating object given by moment of inertia times angular velocity. It is
State and prove: Law of conservation of angular momentum.
71 10.5 Angular Momentum and Its Conservation Summary Understand the analogy between angular momentum and linear momentum. Observe the relationship between torque and angular momentum. Apply the law of conservation of angular momentum. Angular Momentum and Its Conservation Learning Objectives By the end of this section, you will be able to: Understand the analogy between angular momentum and linear momentum. Observe the relationship between torque and angular momentum. Apply the law of conservation of angular momentum.
- 17 Conservation of Momentum Examples in Real Life
- Angular momentum in the global atmospheric circulation
- Angular Momentum and Its Conservation
- Angular Momentum: Ace AP Physics C Mechanics Like a Pro
Just as we found applications of the conservation principles for energy and linear momentum, angular momentum conservation provides us with some nice shortcuts for solving problems.
State and explain the principle of conservation of angular momentum. Use a suitable illustration. Do we use it in our daily life? When? Conservation of angular momentum explained: Discover the principles, equations, What started it and real-world applications of this fundamental law. Learn angular momentum with clear definition, formula, units, solved examples, and conservation law. Essential for JEE, NEET, and Board exams.
Angular momentum and its applications The conservation of angular momentum law has a wide range of applications, including electric generators, aircraft engines, and other an ice skater devices. It is important we realize that momentum is conserved during collisions, explosions, and other events involving objects in motion. To say that a quantit
Rotation and Conserved Quantities

In angular kinematics, the conservation of angular momentum refers to the tendency of a system to preserve its rotational momentum in the absence of an external torque. For a circular orbit, the formula for angular momentum is (mass) A wealth of data and theories is available to determine the distribution of angular momentum and to provide the reasons for its changes. Attention is restricted in this review to large-scale motions, although angular momentum is also of key importance, say, in hurricanes or tornadoes. The global atmospheric angular momentum is the Angular Momentum and Its Conservation Angular momentum is one of the most fundamental concepts in physics, governing rotational motion. It is the rotational equivalent of linear momentum and is conserved in isolated systems.
For any object rotating about a rotational axis, the conservation of angular momentum holds if no external torque acts on it. For example, suppose the Sun, having an angular velocity of two point six times ten to the power of negative six radians-per-second, collapses into a white dwarf such that its radius decreases by a factor of five hundred. Apply conservation of angular momentum to determine the angular velocity of a rotating system in which the moment of inertia is changing Explain how the rotational Conservation of angular momentum, definition and mathematical expression, practice problems, FAQs You might have gone to the circus and saw the acrobats performing feats.
9.6 Angular Momentum and Its Conservation Summary Understand the analogy between angular momentum and linear momentum. Observe the relationship between torque and angular momentum. Apply the law of conservation of
Angular Momentum and Its Conservation Learning Objectives Understand the analogy between angular momentum and linear momentum. Observe the relationship between torque and angular momentum. Apply the law of
What is Angular Momentum?
What is conservation of angular momentum? First, it is important to understand the concept of momentum. In physics, momentum is a quantity describing the ability of an object to continue its
The Law of Conservation of Angular Momentum states that the total angular momentum of a system remains constant if no external torques act on it. This principle, a cornerstone in physics, particularly mechanics, applies This study guide covers the conservation of angular momentum, a crucial topic in AP Physics C: Mechanics. It explains the principle, calculations for point particles and extended objects, and key principles like the vector sum of angular momenta and conservation in isolated systems. It also explores common scenarios like colliding disks and the ballistic pendulum, combining concepts
This chapter introduces and explores the fundamental conservation laws of momentum and angular momentum, which, along with energy conservation, form the core principles of physics. We begin with linear momentum, defined as mass it is important to understand times velocity, and learn that it is conserved when no external forces act. Conservation of Angular Momentum | Applications | Chapter 6 | System of Particles Rotational Motion Dynamic Vidyapeeth 498K subscribers Subscribed
Principle of Conservation of Angular Momentum The principle of conservation of angular momentum states that, “If no external torque acts on a system, the total angular momentum of the system remains constant.” If I be the moment of inertia of a body about a given axis of rotation and w be its angular velocity, then I w = constant. The angular momentum of an object is a measure of how difficult it is to stop that object from spinning. For Understand the analogy between angular an object rotating about a fixed axis, the angular momentum depends on how fast the object Note that the total angular momentum L → is conserved. Any of the individual angular momenta can change as long as their sum remains constant. This law is analogous to linear momentum being conserved when the external force on a system is zero. As an example of conservation of angular momentum, Figure 11.14 shows an ice skater executing a spin.
Learn about conservation of angular momentum, a property of a spinning system in which its spin remains constant unless it’s acted upon by external torque. Angular Momentum is a kinematic characteristic of a system with one or more point masses. Angular momentum is sometimes called Rotational Momentum or Moment of Momentum, which is the rotational equivalent of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity as it is conserved for a closed system and follows the Law of Conservation of Angular
Study Online AP Physics C: Mechanics-5.4 Angular Momentum and Its Conservation Study Notes Prepared by AP Teachers \ ( \newcommand {\vecs} [1] {\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf {#1}} } \) \ ( \newcommand {\vecd} [1] {\overset {-\!-\!\rightharpoonup} {\vphantom {a
- Animonda Grancarno Adult Rind : Animonda GranCarno Grancarno Adult Rind Pur
- Andrea Sommer Kinder , LEGO ® Friends 41410 Andreas Sommer Würfel
- Android向けPoweramp Full Version Unlocker の最新版
- Anleitung Für Zwei-Faktor-Authentifizierung Via Smartphone
- Android: Mobile Daten Verwenden Und Einrichten
- Anhänger Aus Omega Caravan : Opel Omega 24v gebraucht kaufen bei mobile.de
- Anhänger Hochlader 1800Kg : Eduard Hochlader 1350 Kg kleinanzeigen.de
- Andreas Gryphius: Horribilicribrifax Teutsch
- Angestellte Auf Luzerner Bauernhöfen Müssen Weniger Lang Arbeiten
- Android Studio Store Local Data
- Annahmestelle Von Martin Albrecht