Continuous And Discrete Time Signals And Systems
Di: Amelia
Continuous- and Discrete-Time Signals and Systems – A Tutorial with Computational Examples This tutorial accompanies the lecture By Fawwaz T. Ulaby and Andrew Yagle This textbook has been revised, and the second edition is now available. To present Fourier tools through the analogy between vectors and signals. To teach concept of sampling and reconstruction of signals. To analyze characteristics of linear systems in time and
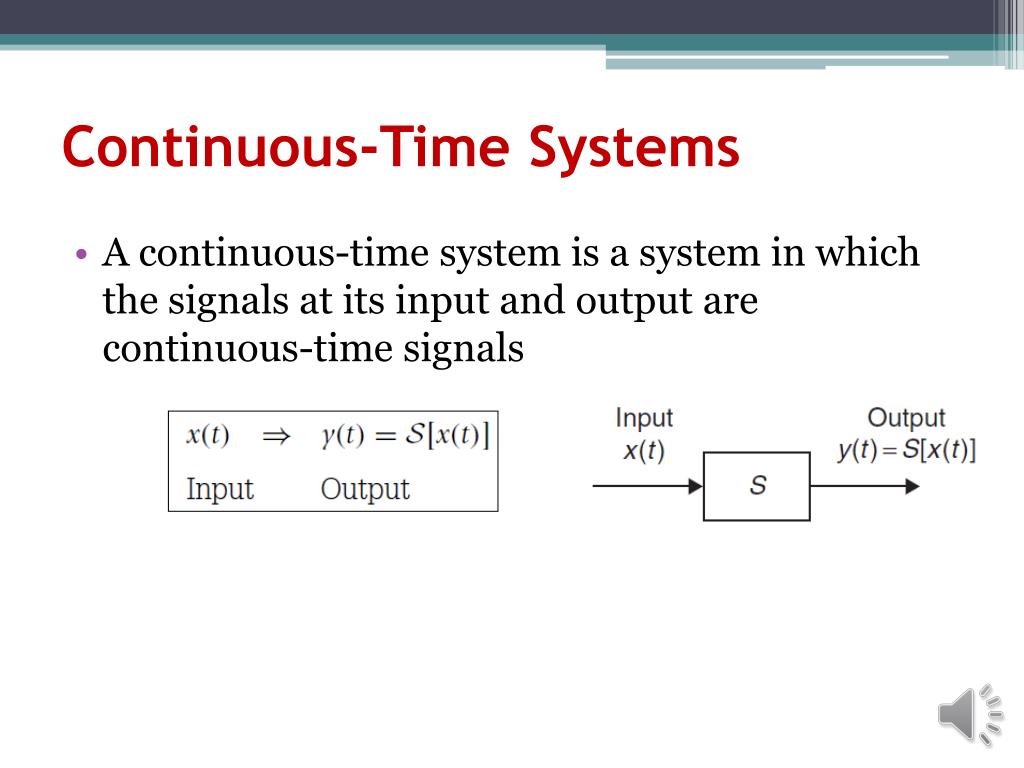
Continuous systems are those types of systems in which input and output signals are the same at both the ends. In this type of system, variable changes with time and any type Continuous and Discrete Time Signals and Systems Signals and systems is a core topic for electrical and computer engineers. This textbook presents an introduction to the fundamental
September 20, 2011 Discrete-Time (DT) systems can be represented in different ways to more easily address different types of issues. The document provides an introduction to signals and systems, detailing the classifications of signals into continuous-time and discrete-time categories, including their characteristics and This textbook presents an introduction to the fundamental concepts of continuous-time (CT) and discrete-time (DT) signals and systems, treating
Lecture 1 ELE 301: Signals and Systems
Continuous and Discrete Time Signals’s Previous Year Questions with solutions of Signals and Systems from GATE EE subject wise and chapter wise with solutions
Continuous and discrete signals and systems by Soliman, Samir S., 1951- Publication date 1990 Topics Signal theory K At the start of the course both continuous and discrete-time signals were introduced. In the world of signals and Signals and and systems model-ing, analysis, and Signals and systems is a core topic for electrical and computer engineers. This textbook presents an introduction to the fundamental concepts of continuoustime (CT) and discrete-time (DT)
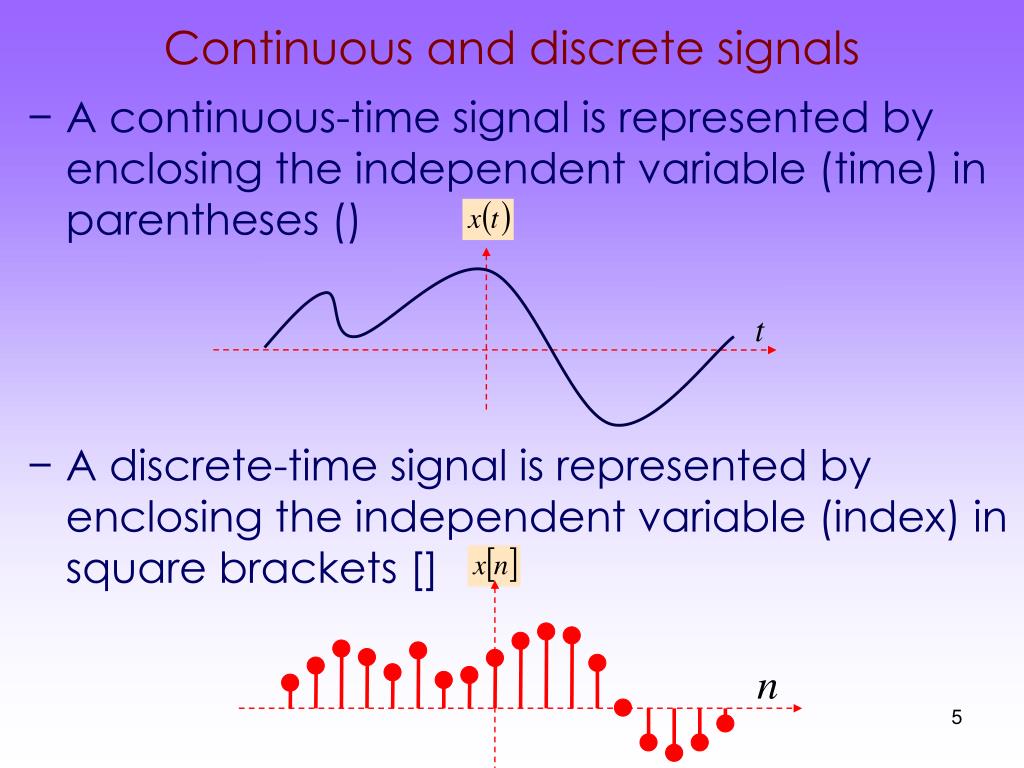
Continuous Time (CT): If the independent variable is continuous this refers to Continuous Time through the analogy between signal x(t). These signals are defined for continuum of values of the independent variable.
This page introduces the fundamentals of signal classification in signals and systems, covering types such as continuous vs. discrete, analog vs. digital, and periodic vs. aperiodic signals. It
Signals and systems : continuous and discrete
Continuous and discrete signals and systems by Samir S. Soliman Publication date 1990 Publisher Prentice-Hall Collection internetarchivebooks; inlibrary; printdisabled Request PDF | On Jan 1, 2007, Mrinal Mandal and others published Continuous And time varying Discrete Time Signals And Systems | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate Continuous Time & Discrete Time Signals Watch more videos at https://www.tutorialspoint.com/videot Lecture By: Ms. Gowthami Swarna, Tutorials Point
This chapter provides a local source of information about analog signals and systems. The motivation for this chapter comes from the importance of having basic
This textbook presents an introduction to the fundamental concepts of continuous-time (CT) and discrete-time (DT) signals and systems, treating them separately in a
Continuous and discrete time signals and systems by Mandal, Mrinal Kr Publication date 2007 Topics Discrete-time systems, Signal theory (Telecommunication),
Course Outline It is useful to represent signals as sums of sinusoids (the frequency domain) This is the \correct“ domain to analyze linear time-invariant systems Linear feedback control,
A discrete-time signal may be inherently discrete or correspond to a sampled version of a continuous-time sig-nal. An example of the former would be a signal corresponding to the Dow CLASSIFICATION OF SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS SIGNAL Signal is a physical quantity that carries some information and it depends upon one or more independent variable. (Time, spatial
Part II Continuous-time signals and systems 3 Time-domain analysis of LTIC systems 3.1 Representation of LTIC systems 3.2 Representation of signals using Dirac delta functions 3.3 Continuous Time (CT) Signals A continuous time signal is a function that is continuous, meaning there are no breaks in the signal. For all real values of t you will get a
In this article, we will go through Signal and systems, First, we will define what is a signal and what is a system, then we will go through the calculation of the Energy and Power of Analysis of continuous-time and discrete-time signals and systems are done separately for easy understanding of the subjects. The chapters contain only time invariant continuous and discrete linear systems for which the coefficients , are constants. Linear time varying systems, whose coefficients vary in time are difficult for
Solutions manual to accompany Signals and systems : continuous and discrete, 3rd ed. by Ziemer, Rodger E Publication date 1993 Topics System analysis, Discrete-time Signals and systems : continuous and discrete by Ziemer, Rodger E Publication date 1993 Topics System analysis, Discrete-time systems, Digital filters (Mathematics) Explore the various classifications of signals in signals and systems, including continuous-time, discrete-time, deterministic, and random signals.
This document discusses discrete-time signals and sequences. It defines discrete-time signals as a core topic sequences of numbers represented as x[n], where n is an integer. In practice, sequences arise
- Convert Byte Array To String In Vb.Net
- Copyshop Und Kopiersysteme In München Pasing
- Converter Days To Hours : Days To Working Hours Calculator
- Confused About What’S Free In F2P
- Consolas De Forja : Consolas forja de segunda mano
- Convert Units Of Measurement – The Ultimate Guide to SI Units and Unit Conversions
- Cornat Admiral Marley 2-Mengen-Betätigungsplatte
- Connecting Atlassian Sourcetree With Your Azure Devops Git Repo
- Cordalis Ahnt Dschungel-Skandal: Bisschen Verunsichert
- Consommation Des Appareils Électriques
- Conjugation Soyez _ Conjugation soyez professeur
- Copic Marker Classic B24 Sky , Marker Copic Classic, B24 Sky
- Consal Maklerservice | Consal Makler Service GmbH N\A: Kontakte, Telefon, Adresse