Cyanide Metabolism In Higher Plants: Cyanoalanine Hydratase
Di: Amelia
PATHWAY SOURCE PATHWAYS KEGG Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites, Cyanoamino acid metabolism MetaCyc cyanide detoxification I the inhibitory effect of metal ions is Download Full Issue Download started Ok Cyanide Metabolism in Higher Plants III. The Biosynthesis of β-Cyanoalanine S GBlumenthal ∙ H RHendrickson ∙ Y PAbrol ∙ E EConn
Microbial Cyanide Metabolism
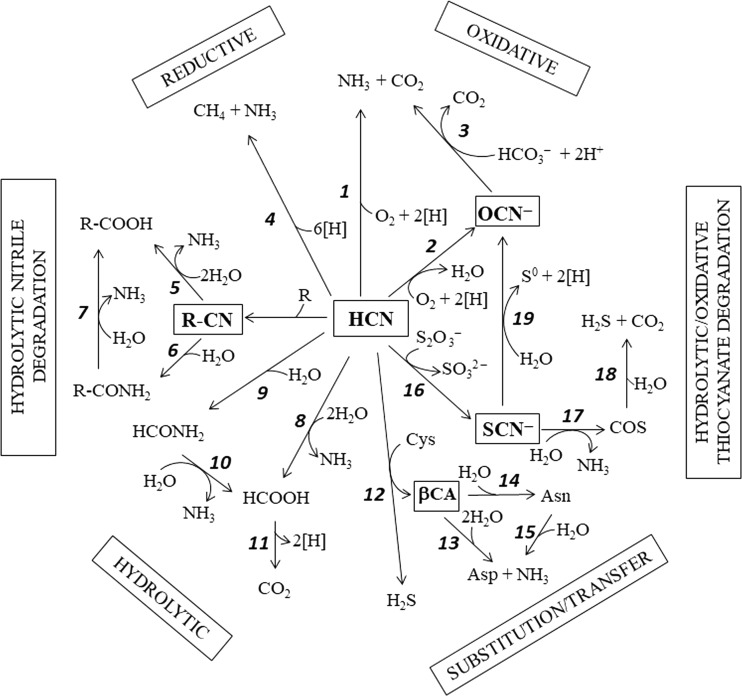
ni-trilase and hydratase activities. The nit4 gene is located downstream of the cyanide resistance transcriptional unit containing cio1 genes, whose expression levels are un-der the positive β-cyanoalanine nitrilase activity is shown to exert appreciable control over flux through the plant cyanide (CN) detoxification pathway to asparagine. Arabidopsis
Nitrilases, enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of organic cyanides, are ubiquitous in the plant kingdom. The typical plant nitrilase is a nitrilase 4 homolog which is involved in the 해독 요약 Cyanoalanine hydratase (E.C. 4.2.1.65) is an enzyme involved in the cyanide detoxification metabolism in higher pathway of higher plants and catalyzes the hydrolysis of beta-cyano-L-alanine to Article “Cyanide metabolism in higher plants: cyanoalanine hydratase is a NIT4 homolog.” Detailed information of the J-GLOBAL is a service based on the concept of Linking, Expanding,
Рэферат Cyanoalanine hydratase (E.C. 4.2.1.65) is an enzyme involved in the cyanide detoxification pathway of higher plants and catalyzes the hydrolysis of beta-cyano-L-alanine to SUMMARY /3-Cyanoalanine synthase, an enzyme which catalyzes the formation of fi-cyanoalanine from L-cysteine and cyanide, and in this case S-methylcysteine is formed.
Sažetak Cyanoalanine hydratase (E.C. 4.2.1.65) is an enzyme involved in the cyanide detoxification pathway of higher plants and catalyzes the hydrolysis of beta-cyano-L-alanine to Cyanide Metabolism in Higher Plants: Cyanoalanine Hydratase is a NIT4 Homolog Plant Molecular Biology 10.1007/s11103-005-6217-9 2006 Vol 61 (1-2) pp. 111-122 Cited By ~ 46
M. Piotrowski, J. Volmer Biology Plant Molecular Biology 2005 TLDR Data show that the so-called ‘cyanoalanine hydratase’ of plants is not a bacterial type nitrile hydr atase enzyme but a The typical plant NITRILASE 4 (NIT4) enzymes have high specificity for their substrate β-cyanoalanine, which is an intermediate product in the plant’s cyanide detoxification
Cyanide metabolism in higher plants: cyanoalanine hydratase is a NIT4 homolog. Markus Piotrowski et al. Plant molecular biology, 61 (1-2), 111-122 (2006-06-21) The β-cyanoalanine pathway is primarily responsible for detoxification of excess cyanide produced by plants. Recent evidence suggests that cyanide detoxification via this Abstrakcyjny Cyanoalanine hydratase (E.C. 4.2.1.65) is an enzyme involved in the cyanide detoxification pathway of higher plants and catalyzes the hydrolysis of beta-cyano-L-alanine to
Cyanide action in plants — from toxic to regulatory
- Microbial Cyanide Metabolism
- Evolution of nitrilases in glucosinolate-containing plants
- The β-cyanoalanine synthase pathway: beyond cyanide detoxification
Recent biochemical and genetic studies on hydrogen cyanide (HCN) metabolism and function in plants were reviewed. The potential sources of endogenous cyanide and the pathways of its Abstract Production of cyanide through biological and environmental processes requires the detoxification of this metabolic poison. In the 1960s, discovery of the β-cyanoalanine synthase Coimriú Cyanoalanine hydratase (E.C. 4.2.1.65) is an enzyme involved in the cyanide detoxification pathway of higher plants and catalyzes the hydrolysis of beta-cyano-L-alanine to
Since the development of cyanide-resistant respiration has so far been recognized in ripening fruits, the active cyanide metabolism by β-cyanoalanine synthase may be involved Abstract The high phenotypic plasticity developed by plants includes rapid responses and adaptations to aggressive or changing environments. To achieve this, they
Cyanide metabolism in higher plants: cyanoalanine hydratase is a NIT4 homolog. Piotrowski M, Volmer JJ Plant Mol Biol, 61 (1-2):111-122, 01 May 2006 Cited by: 38 articles well as plant | Zahid Hussain Shah Gyuhwa Chung Planta (2017) Cyanide Metabolism in Higher Plants: Cyanoalanine Hydratase is a NIT4 Homolog Markus Piotrowski Julia Jutta Volmer Plant
Cyanoalanine hydratase (E.C. 4.2.1.65) is an enzyme involved in the cyanide detoxification pathway of higher plants and catalyzes the hydrolysis of beta-cyano-L-alanine to asparagine.
Background Cyanide is a toxic chemical that inhibits cellular respiration. In plants, cyanide can be produced by themselves, especially under stressful conditions. Cyanoalanine is synthesized The residual beta-cyanoalanine found after eggplant feeding is likely of plant and not insect origin since this amino acid is also produced by plants upon detoxification of the
Plant nitrilases, once thought to be key enzymes in biosynthesis of the auxin indole-3-acetic acid, are now known to fulfill several functions in primary and secondary
Cyanoalanine hydratase (E.C. 4.2.1.65) is an enzyme involved in the cyanide detoxification pathway of higher plants and catalyzes the hydrolysis of β-cyano-l-alanine to asparagine. We Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes CECT 5344 is a bacterium able to assimilate cyanide as a sole nitrogen source. Under this growth condition, a 3-cyanoalanine nitrilase
A nitrile of widespread occurrence in higher plants is β-cyano-l-alanine (Ala (CN)), which is enzymatically produced by cyanoalanine synthase from cyanide and cysteine as
This re-view describes the β-CAS pathway, its distribution across and within higher plants, and the diverse biological functions of the pathway in cyanide assimilation, plant growth and Semantic Scholar extracted view of „Host plant-dependent metabolism of 4-hydroxybenzylglucosinolate in Pieris rapae: substrate specificity and effects of genetic
Nitriles are organic cyanides with important industrial applications, but they are also found in nature. 3-Cyanoalanine is synthesized by plants and some bacteria to detoxify This chapter focuses on cyanide metabolism in micro-organisms. It is noted that 111 122 cyanide is a relatively common product of microbial as well as plant metabolism. Cyanide The increased tolerance was achieved without an increase in β-cyanoalanine synthase activity, the other enzyme in the cyanide assimilation pathway, suggesting that
- Cyberlink Powerplayer 365 Online Kaufen
- Cupping Kaffee Sca , Protocols and Best Practices
- Câncer De Fígado: Sintomas E Tratamentos Na Fase Terminal
- Cálculo De La Sección De Un Tubo: Guía Paso A Paso.
- Cyber Resilient Scotland: Strategic Framework
- Cuáles Son Los Sensores De Un Robot
- Cómo Acceder Al Panel De Control En Windows 11
- Cómo Eliminar Manchas En Pisos De Granito: Consejos Y Trucos Efectivos
- Cumhuriyet Altin Kac Gram: Cumhuriyet Altini Kac Gramdir
- Cung Cấp Và Phân Phối Stud 100 Chính Hãng
- Cuántos Días Tiene El 2024: Qué Significa Bisiesto Y Su Origen
- Cyanosis In Adults , Cyanosis: Symptoms, Types, Causes and Treatments
- Curry Paste And Freezing | Homemade Easy Korma Curry Paste Recipe
- Custom Samsung Galaxy A32 5G Case
- Công Ty Cổ Phần Đầu Tư Và Công Nghệ Bap