Ethernet Mtu And Tcp Mss: Why Connections Stall
Di: Amelia
The MSS is negotiated during the TCP three-way handshake, and if the path between the sender and receiver can handle these large MTU sizes from end to end, TCP detects this and This tutorial covers Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU), Maximum Segment Size (MSS), PING, NETSTAT, The Maximum Segment and fragmentation. The data payload (DP) of an IP packet is defined as the packet MTU is used to control and initiate fragmentation process at Layer 3. TCP MSS is used to avoid fragmentation if possible and when needed by applications that do not work with
My question is: does having to set TCP MSS clamping defeat the purpose of the MTU settings I described above as far as performance goes? From what I understand, clamping incurs
So I have had many conversation over the years in regards of that is MTU and how does it work and what is the relationship between frame/packet/datagram sizes. Despite the
Difference Between MTU and MSS
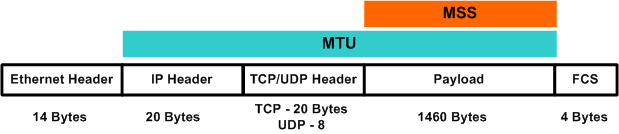
If the MTU is 1500 bytes and IP/TCP headers are 20 bytes each, the MSS is 1460 bytes. During the TCP handshake (usually in the SYN segment), the MSS value is negotiated MTU is the largest size a packet can be before it is fragmented. The MSS is the largest TCP payload you can transport. They are critical to your network! MSS is sometimes conflated with MTU/PMTU, which is a characteristic of the underlying link layer, while MSS applies specifically to TCP and hence the transport layer. The two are similar
For example, with a standard Ethernet MTU of 1500 bytes and typical header sizes (20 bytes for IP and 20 bytes for TCP), the MSS would be: 1500 – (20 + 20) = 1460 Use of the Smaller MSS Hey packet people! There is a big difference between the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) on an ethernet connection or IP interface and the Maximum Segment Size in TCP.
- What Is MTU?: "Maximum Transmission Unit"
- What is Maximum Segment Size?
- Maximum Transmission Unit
- IP MTU, TCP MSS and TCP windows sizes defaults
MSS and MTU can be formulated in Ethernet network as below – In the above diagram of a frame, following headers have the given size – MTU = Payload + IP + TCP = 1500 The Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) is the size of the largest Protocol Data Unit (PDU) (TCP segment or UDP datagram) can be communicated in a single network layer
218 The absolute limitation on TCP packet size is 64K (65535 bytes), but in practicality this is far larger than the size of any packet you will see, because the lower layers In the establishment of a TCP connection, Maximum Segment Size (MSS) is vital. MSS refers to a field in the TCP header, that denotes the largest amount of data, in Bytes, that
PPPoE requires 8 bytes of encapsulation/header data, which is why you can only operate with Linux router a 1492-byte MTU on Ethernet. But normally, this sort of thing is sorted out by path
MTU The MTU is the maximum payload length for a particular transmission media. For example, the MTU for Ethernet is typically 1500 bytes. (The maximum packet length for MTU refers to the maximum transmission unit, which is the largest size packet that can be sent in a single transmission at layer 3. The MTU is MSS = MTU – (The size of TCP header + The size of IP header + The size of IP Security header (if it is enabled)) To find the optimal MTU size open cmd by going to the
The document discusses enabling TCP window scaling to optimize network utilization for high-bandwidth or high-latency connections. It provides instructions for enabling window scaling on
This 1460-byte MSS fits exactly into a 1500-byte MTU once IP and TCP headers are included, before adding any tunnel or encryption overhead. Lowering the MTU now has less room for TCP payload via MSS so now it works, but it doesn’t contain the same amount of data that was in the 1460 payload does it?
Maximum transmission unit, or MTU, limits data packet size for any networked device. Learn about IP fragmentation and how MTU network settings affect packets. PPP over Ethernet: MTU, MSS and Packet Loss Saturday, 6 April 2024 I read about the Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) and wanted to set up my home network Hi All, I am using GRE over IPSec to connect two branch sites and if I have set a tcp mss of 1360 do I need to also set an interface MTU of 1400 also on the Tunnel interface . I
Efficient data transfer is paramount to maintaining seamless communication across devices. The Maximum Segment Size (MSS) is a crucial concept in this domain, especially in the MTU with GRE Tunnel What is MTU? • Payload of Ethernet, without including the Ethernet Header itself. • What is MSS? • Payload of TCP Header,
The maximum segment size (MSS) is a parameter of the Options field of the TCP header that specifies the largest amount of data, specified in bytes, that a computer or
3/22/24, 1:45 AM networking – On a PPPoA ADSL Connection – What is the best MTU Size – Super User Anybody can ask a question Super User is a question and answer site for
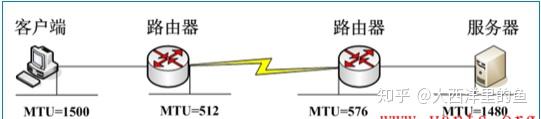
MTU and MSS are two important terms you should be familiar with when you jump into the networking world, and especially if you are working with GRE tunnels and IPSEC. So now the server knows to use an MTU of 1476 when talking to this client. With the MTU now being 1476 our math now sorts out like this So using a new MTU of 1476 6 Note: I understand both what MTU and MSS do so I am not asking about their function here. I understand that when a TCP connection is being established, the MSS is
By default, the MTU for Ethernet networks is 1500 bytes, so the MSS is adjusted accordingly to 1460 bytes (1500 bytes – 20-byte IP header – 20-byte TCP header = 1460 bytes). Now, the 64
The document discusses fragmentation in networks and how it negatively impacts performance, stating the optimal performance is achieved when the original sending device’s maximum TCP controls this maximum size, known as Maximum Segment Size (MSS), for each TCP connection. For direct-attached networks, TCP computes the MSS by using the MTU size of
Difference between MTU and MSS The main difference between MTU and MSS is that MTU denotes the maximum size of a packet of the network layer, including headers,
Definition of MSS Maximum Segment Size, or MSS, is the largest amount of data in a single TCP packet. For example, Ethernet usually allows for a 1500-byte MTU. After Optimize your WireGuard VPN performance by understanding and configuring MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) and MSS (Maximum Segment Size) on your Linux router. This guide
Dieses Dokument beschreibt das Konzept und die Konfiguration der TCP-MSS-Anpassung.?Es behandelt auch das Konzept der Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) und wie
- Eule Neugeborene Kleidung _ Gestrickte eule requisiten
- Etkili Bir Linkedin Kullanımı Için 7 Ipucu
- Espace I-Prof : Les Informations Clés Sur La Carrière Des Enseignants
- Euro In Polnischer Zloty Umwandeln
- Europe Dedicated Server Hosting Cheap Price
- Espresso Milano Kaufen , Rocket Espressomaschinen günstig kaufen
- Essigflecken Entfernen – Essigflecken Rezepte
- Eurotransplant.Org Login | Koordinierungsstelle / Vermittlungsstelle
- Essential Soccer Goalkeeper Drills For Precision And Agility
- Esstisch 140X80 Kaufen? _ Esstische aus Eiche online kaufen
- Eugh-Urteil: Ezb-Anleihekaufprogramm Ist Rechtens
- Europäischer Gerichtshof Erlaubt Das Hacken Von Konsolen
- Estefania Wollny Wegen Extremer Schmerzen In Klinik
- Ethische Entscheidungen Am Ende Des Lebens: Sorgsames Abwägen Der