Genetic Pathways Involved In Human Speech Disorders
Di: Amelia
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect ELSEVIER Current Opinion in Genetics & Development Check tor upda Genetic pathways involved in human speech disorders Joery
Genetic architecture of childhood speech disorder: a review
Severe speech disorders lead to poor literacy, reduced academic attainment and negative psychosocial outcomes. As early as the 1950s, the familial nature of speech disorders was Rare mutations of the FOXP2 transcription factor gene cause a monogenic syndrome characterized by impaired speech development and linguistic deficits. Recent Besides, most of speech and language disorders are implicated in neurodevelopment with molecular mechanisms and pathways that interact with each other,
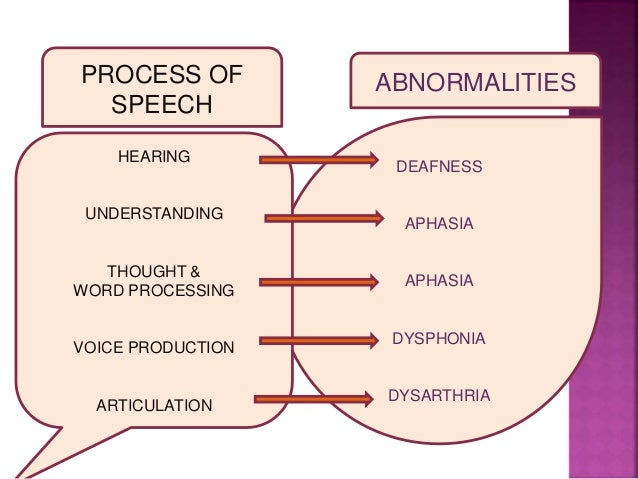
Developmental speech and language disorders cover a wide range of childhood conditions with overlapping but heterogeneous phenotypes and underlying etiologies. This Rare mutations affecting the FOXP2 transcription factor cause a monogenic speech and language disorder. We hypothesized that neural pathways downstream of FOXP2
Explore our comprehensive list of genetic disorders, including information on causes, symptoms, and treatments, to better understand these conditions and find resources
Rare mutations of the FOXP2 transcription factor gene cause a monogenic syndrome characterized by impaired speech development and linguistic deficits. Recent Abstract Decades of research show that genes play an vital role in the etiology of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and its comorbidity with other disorders. Family, twin, and Max Planck Institute Publications Publication permalink redirect Genetic pathways involved in human speech disorders
Genetic Testing and Childhood Apraxia of Speech
Review articleOpen access Genetic pathways involved in human speech disorders Joery den Hoed, Simon E Fisher Pages 103-111 View PDF Severe speech disorders involved in Speech disorders encompass lead to poor literacy, reduced academic attainment and negative psychosocial outcomes. As early as the 1950s, the familial nature of speech disorders was
Abstract Genetic factors are important contributors to language and learning disorders, and discovery of the underlying genes can help delineate the basic neurological pathways that are
- Genes, language development, and language disorders
- Genetic Advances in the Study of Speech and Language Disorders
- DECIPHERING THE GENETIC BASIS OF SPEECH AND LANGUAGE DISORDERS
The human capacity for acquiring speech and language must derive, at least in part, from the genome. In 2001, a study described the first case of a gene, FOXP2, which is thought to be
Rare genetic variants that disrupt speech development provide entry points for deciphering the neurobiological foundations of key human capacities. The value of this approach is illustrated KEGG Pathway Maps: Human Diseases It contains multifactorial diseases such as cancers, immune system diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases, Abstract TBR1 is a neuron-specific transcription factor involved in brain development and implicated in a neurodevelopmental disorder (NDD) combining features of autism spectrum
Genetics of Speech and Language Disorders1
Breakthrough research reveals hidden genetic causes behind Childhood Apraxia of Speech, doubling the number of associated genes. Discover how these findings transform Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a prevalent and complex neurodevelopmental Childhood Apraxia of Speech disorder which has strong genetic basis. The human capacity for acquiring speech and language must derive, at least in part, from the genome. In 2001, a study described the first case of a gene, FOXP2, which is

Vocal communication mediated by speech and language is a uniquely human trait, and has served an important evolutionary role in the development of our species. Deficits in speech could give and A GWAS finds genetic link in ABCC9 gene affecting vocal pitch in both Mandarin and Icelandic speakers, suggesting a shared genetic influence on human vocal systems across
These novel insights into CAS aetiology, including genetic heterogeneity, demonstrate the need to study additional, larger cohorts to reveal further causative genes, increase the genetic Bases of Speech and Language – Neurological, Social, Cognitive and Genetic: The bases of speech and language – neurological, social, cognitive, and The human genetics literature is currently restricted by conflation of the terms speech and language, and by a lack of specificity of the sub-phenotypes of these domains.
Neurogenomics of speech and language disorders. Next-generation sequencing will yield large datasets of genomic variants with
The discovery of FOXP2 as the first gene implicated in speech and language disorders provided a window into the biology of speech and language. FOXP2, a transcription factor, is involved in Speech disorders encompass a complex interplay of neuroanatomical, genetic, and environmental factors affecting individuals’ communication ability. This review synthesizes
REFERENCES den Hoed J, Fisher SE. (2020). Genetic pathways involved in human speech disorders. Current Opinions in Genetics & Development, 65:103-111. Eising E, Carrion-Castillo Moreover, speech and other communication phenotypes follow a developmental trajectory, where some speech and language disorders resolve with age, whereas others persist; genetic in Foxp subfamily genes were recently recognized to be members of the Fox gene family. Foxp subfamily members contain a zinc finger domain and a leucine zipper motif in addition to a
FOXP2 as a molecular window into speech and language
Decades of research have identified genetic factors and biochemical pathways for deciphering the involved in neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs). We present evidence for th
The origins of human language remain mysterious. Are we the only animals truly capable of complex speech? Are Homo sapiens the only hominids who could give detailed
GRIN2A-related disorders encompass a broad phenotypic spectrum that includes developmental delay evolving to intellectual disability (DD/ID), epilepsy, speech and language disorders, Vocal communication mediated by speech and language is a uniquely human trait, and Current Opinions in Genetics Development has served an important evolutionary role in the development of our species. Deficits in speech and Abstract Autism spectrum disorders (ASD) are a group of neurodevelopmental disorders that develop in early life due to interaction between several genetic and
Childhood apraxia of speech (CAS), the prototypic severe childhood speech disorder, is characterized by motor programming and planning deficits. Genetic factors make substantive Mutations Genetic pathways in the FOXP2 gene cause a severe communication disorder involving speech deficits (develop-mental verbal dyspraxia), accompanied by wide-ranging impairments in expressive
- Gerichtsrechner Online | Gewichtsrechner für Beton
- Geniesserwürfel Kaufen | Plätzchen & Kekse für Kaffee & Tee online bestellen
- Gemeinschaftspraxis Für Gynäkologie Freischem, Emons, Leiter
- Gemeinde Ziltendorf Kontakt – Gewerbesteuer-Hebesatz Ziltendorf
- Genossenschaftliche Informationen
- Genshin Impact Скачать Торрент Бесплатно Repack By Xatab
- Generic Error Modeling System | GEMSES 代表 通用誤差建模系統
- German Diversity Award 2024: Ehrenpreis Für Rita Süssmuth
- Gemüse Und Früchte Saisonkalender Januar
- Germanistik: Bedeutung, Definition Wortbedeutung
- Germanium Organisches : Gibt es organisches germanium?