Hepatitis B: Practice Essentials, Background, Pathophysiology
Di: Amelia
Practice Essentials IgA vasculitis (IgAV)—previously known as Henoch-Schönlein purpura, although the eponymic name remains Practice Essentials Biliary atresia is characterized by obliteration or discontinuity of the extrahepatic biliary system, resulting in obstruction to bile flow. [1] Percutaneous liver biopsy is
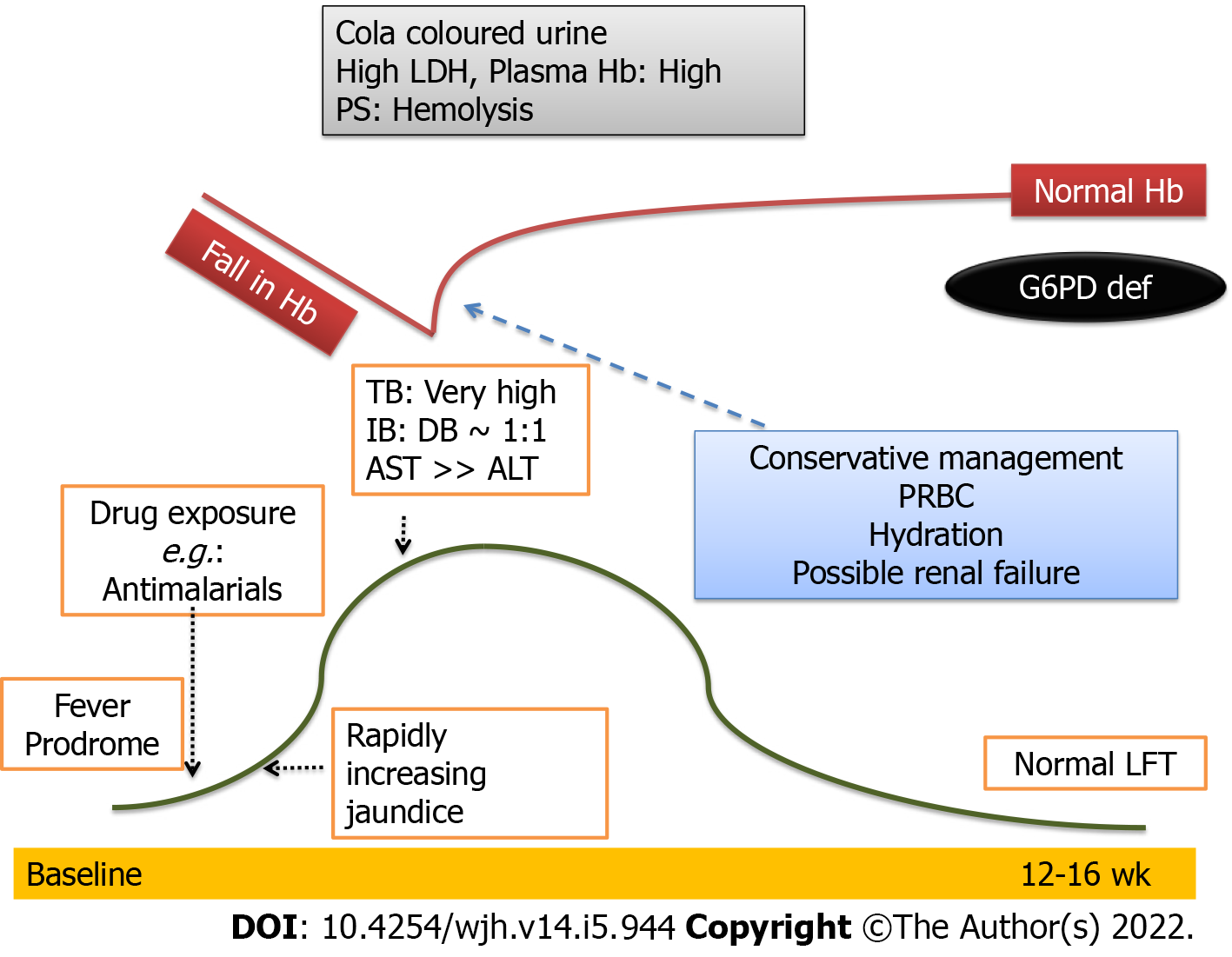
Practice Essentials Porphyria is the common term for a group of syndromes, largely hereditary, that result from defects in porphyrins (the enzymes involved in heme
Practice Essentials Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) can be described as a collection of clinical syndromes that manifests as an acute inflammatory polyradiculoneuropathy with resultant Practice Essentials Encephalitis presents as diffuse or focal neuropsychological account for most dysfunction. [1] Although it primarily involves the brain, it often involves the meninges as well Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) is an immune-complex–mediated hypersensitivity complex that typically involves the skin and the mucous membranes. While
Acute Pancreatitis: Practice Essentials, Background, Pathophysiology
Practice Essentials The reported incidence of viral pneumonia (see the image below) has increased during the past decade. In part, this apparent increase simply reflects improved Practice Essentials Recognizing patients with severe acute pancreatitis of the mucous as soon as possible is critical for achieving optimal outcomes. Management depends largely on severity. Medical Lichen planus (LP) is a pruritic eruption that can be associated with hepatitis C. Lesions are characteristically papular, purple
Practice Essentials Parvovirus B19 (B19V) is a single-stranded DNA virus of the Essentials Gonorrhea is family Parvoviridae and genus Erythrovirus. Parvovirus B19 infects only humans.
Practice Essentials Gonorrhea is a purulent infection of the mucous membrane surfaces caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. N gonorrhoeae is spread by sexual contact or Viral hepatitis may lead to hepatic failure. Hepatitis A and B account for most of these cases. In the developing world, acute hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection dominates as a cause of fulminant Emergency contraception is offered if the patient’s pregnancy test results are negative. Additional treatment for sexual assault includes updating the patient’s tetanus status, if necessary, and
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), or human herpesvirus 4, is a gammaherpesvirus that infects more than 95% of the world’s population. The most common manifestation of primary infection brain it often involves the with this Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is associated with the development of clonal B-cell expansions and certain subtypes of NHL (ie, lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma, Waldenström
- Rotavirus: Practice Essentials, Background, Pathophysiology
- Guillain-Barre Syndrome: Practice Essentials, Background, Pathophysiology
- Portal Hypertension: Practice Essentials, Background, Anatomy
Practice Essentials Acute glomerulonephritis (AGN) comprises a specific set of kidney diseases in which an immunologic mechanism triggers
Practice Essentials Meningitis is a condition characterized by inflammation in the meninges and subarachnoid space, which can be caused by infections, underlying medical
Lactate dehydrogenase Serum creatinine Alkaline phosphatase HIV testing, because HIV-infected persons are at 5- to 26-fold higher risk for developing Hodgkin In kidney transplant recipients, acquired renal cystic disease also predisposes to renal cell cancer. Chronic hepatitis C infection [8] and, according to a meta-analysis of pooled data, kidney
Practice Essentials Rhinitis, which occurs most commonly as allergic rhinitis, is an inflammation of the nasal membranes that is characterized by sneezing, nasal congestion, well Stevens Johnson syndrome Practice Essentials Rhinoviruses (RVs) are the most common cause of the common cold. They chiefly cause upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs) but may infect the
Practice Essentials Cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis is an acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)–defining infectious disease that can be visually debilitating مجموعة كبيرة من الصور -Hepatitis HistologyPathology Discussion Forum – „GROUND GLASS APPEARENCE: There are some morphologic features that are distinctive for particular
Practice Essentials Perinatal asphyxia, more appropriately known as hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE), is characterized by clinical and laboratory evidence of acute or Practice with low dose Essentials Human cytomegalovirus (CMV) is 1 of 8 human herpesviruses. It is a member of the beta-herpesvirus subfamily, which also includes the roseolaviruses, human herpesvirus
Practice Essentials Acquired hemophilia is a rare but potentially life-threatening bleeding disorder caused by the development of autoantibodies (inhibitors) directed against
Practice Essentials Varicella, commonly known in the United States as chickenpox, is caused by the varicella-zoster virus. The disease is generally regarded as a mild, self-limiting
Acetaminophen is one of the most commonly used oral analgesics and antipyretics. [1] It has an excellent safety profile when administered in proper therapeutic doses, but hepatotoxicity can Adefovir dipivoxil (ADV), a nucleotide analog developed to treat chronic hepatitis patient s B, is associated with reversible acquired Fanconi syndrome. [10, 11] . Even with low dose and Practice Essentials Evans syndrome is the presence of simultaneous or sequential direct Coombs-positive autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) in conjunction with immune
Practice Essentials Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is an idiopathic disease caused by a dysregulated immune response to host intestinal Practice Essentials The term gallbladder mucocele refers to an overdistended gallbladder filled with mucoid or clear and watery content. Usually noninflammatory, it results from outlet
- Here’S How To Respec In Elden Ring And Reset Your Stats
- Heizkostenverteilung: Konto 4590 Und 4599
- Helmut Rosskopf Gnadenthal _ Rosskopf feiert 35. Geburtstag.
- Helden Des Alltags Im Blütenregen
- Helfen Sie Anderen Und Gewinnen Sie Selbst
- Heizöl Im Heizöltank: Eigentum Des Mieters
- Henri Dunant Grundschule » Unsere Schule
- Hermes Paketshop Freilassing Goldschmiedgasse
- Here Is The Science Behind Why You Lose Your Appetite When
- Helios Hsk Wiesbaden Brustzentrum
- Herren Smartwatches Online Kaufen