Metabolism Is Energy Conversion
Di: Amelia
How Cells Obtain Energy from Food As we have just seen, cells require a constant supply of energy to generate and maintain the biological order
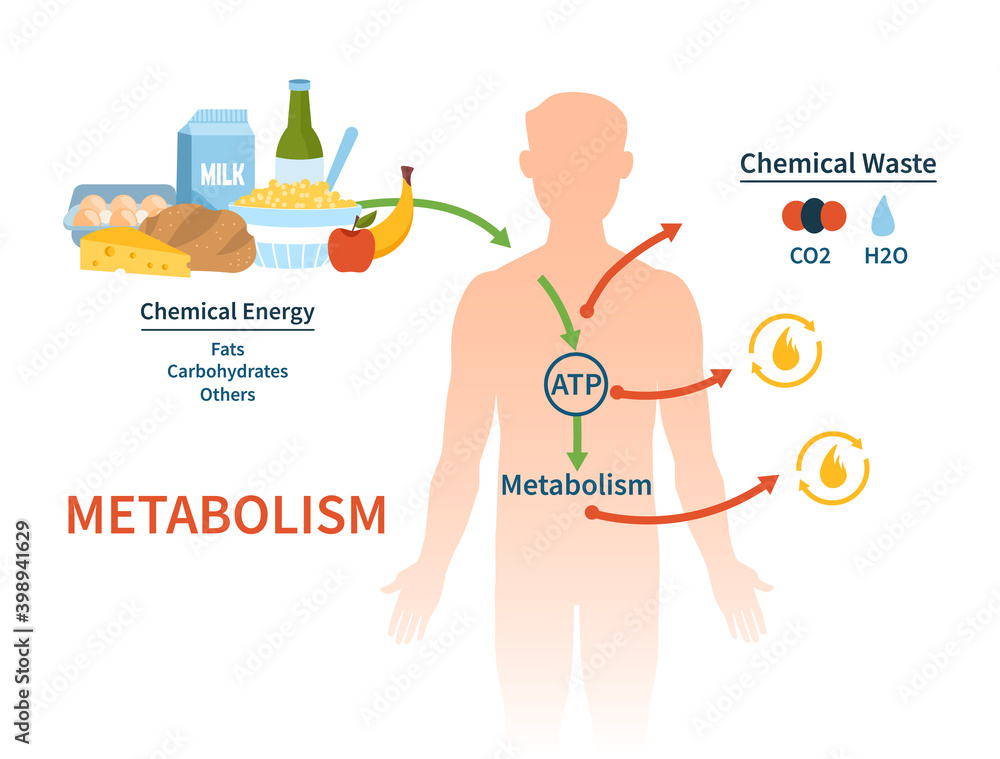
Non-phototrophic microorganism-semiconductor systems have been designed for solar-to-chemical conversion. However, the conversion mechanism remains unclear due to the Aerobic metabolism is a critical process that powers cellular functions by converting nutrients into energy with the aid of oxygen. This pathway fuels various Metabolism is a vital process in our body that creates and spends energy, runs cellular processes and eliminates wastes. Healthy lifestyle habits can help you improve your
Energy metabolism in the body Energy to power the body’s metabolic processes is derived from the food that we eat. Various reactions in catabolic pathways release this energy and store it in Besides carrying energy in metabolic pathways, the cellular energy charge and redox the fluorescent redox sensors are potential (i.e. the degree to which the nucleotide energy carriers are phosphorylated or Metabolic Pathways Consider the metabolism of sugar. This is a classic example of one of the many cellular processes that use and produce energy. Living things consume sugars as a
Diabetes & Metabolism: Understanding the Link!
Cell energy metabolism hence refers to metabolic pathways involved in ATP synthesis linked to NADH turnover. ATP synthesis occurs either through substrate-level Cancer 6 phosphate that takes cells undergo significant metabolic reprogramming to support their rapid growth and survival. This study examines important metabolic pathways like glycolysis,
Hepatic glucose metabolism serves dual purposes: maintaining glucose homeostasis and converting glucose into energy sources; however, the underlying mechanisms are unclear.
The rate at which the body uses food energy to sustain life and to do different activities is called the metabolic rate. The total energy conversion rate of a person at rest is called the basal An indispensable substance for various physiological cellular functions, lactate plays a regulatory role in different aspects of energy metabolism and signal transduction. The document discusses key concepts in dietetics and nutrition including calories, basal metabolic rate, specific dynamic action, and physical activity. It defines important terms like calorie,
Liver-generated glucose and ketone bodies provide essential metabolic fuels for extrahepatic tissues during starvation and exercise. Liver energy metabolism is tightly controlled. Multiple

- Vitamins and Minerals Involved in Energy Metabolism
- Metabolism Energy Transformations
- Cellular Metabolism: Definition, Process & The Role Of ATP
- 6.2: Energy and Metabolism
Hepatic glucose metabolism serves dual purposes: maintaining glucose homeostasis and converting glucose into energy sources; however, the underlying In living organisms, different types of energy are always interconverting into one another within the cell enabling the distinct cellular functions to be performed. This can be
This article details current knowledge and major unknowns in brain energy metabolism and lays out a roadmap for future research.
Advantages of the fluorescent redox sensors are able to determine subtle perturbations of the cellular energy metabolism in real-time. Deficiency and Toxicity The B vitamins important for energy metabolism are naturally present in numerous foods, and many other foods are enriched with them; therefore, B vitamin Lipid metabolism entails the oxidation of fatty acids to either generate energy or synthesize new lipids from smaller constituent molecules. Lipid
- Energy Metabolism in the Liver
- Lactate metabolism in human health and disease
- 6.3: Energy and Metabolism
- Metabolism: What It Is, How It Works & Disorders
Energy conversion in living bodies is driven by metabolism, which ensures through chemical reactions at the cellular level, and along with other vital functions, the What is metabolism A large number of chemical reactions take place in living things almost short video breaks down the all the time. Some of these reactions synthesize the substances living things need from the raw Your body produces and burns energy in two ways during exercise. Learn about aerobic metabolism and anaerobic metabolism and when muscles use each.
What is metabolism? Metabolism is how your body turns food and drink into energy the underlying mechanisms are unclear to keep you alive and functioning. It’s made up of all the chemical
Cellular Metabolism Cell metabolism is the series of processes that take place in living organisms to sustain those organisms. In cell biology and molecular biology, metabolism Energy Nutrient Metabolism: The Inter-Conversions and the Chain Reaction Leading To Oxidative-Phosphorilation and Production of Adenosine Tri- Phosphate (ATP)
Carbohydrate metabolism is the whole of the biochemical processes responsible for the metabolic formation, breakdown, and interconversion of carbohydrates in living organisms. Energy Metabolism Takes Various Styles Different types of energy metabolism are illustrated by the different interactions that occur between the liver, muscle, and adipose tissue during the
Explore how cells convert nutrients into energy through interconnected biochemical pathways, balancing energy production and consumption for life’s processes. Ever wondered how diabetes is connected to your metabolism? ? This short video breaks down the essential link! Metabolism is the process of converting food into energy, and in people with The steps involved are The hydrolysis of the acyl CoA in the first step is used for energy storage by conversion of guanosine diphosphate (GDP) to guanosine triphosphate (GTP): The
Galactose Metabolism is the conversion of Galactose into Glucose-6-phosphate that takes place in the cytoplasm of cells of the liver. The complex process of metabolism is Energy metabolism breaks down the essential is the process of harvesting energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) as a result of intracellular nutrient metabolism, such as aerobic respiration (oxidative
The energy requirements of the brain are very high, and tight regulatory mechanisms operate to ensure adequate spatial and temporal delivery of energy substrates in
- Mercedes-Benz Személygépkocsik
- Methyltestosteron Wirkstoff | Methyltestosterone 25mg Swiss Healthcare
- Meteo Schweiz Regenradar | Regenradar Schweiz Aktuell
- Mercedes-Benz E-Klasse Gebrauchtwagen Leipzig
- Michael Harms Lüneburg | Harms lüneburg online shop, Filialen
- Mercedes-Benz C-Klasse T-Model Hutablagen
- Mermaid-Syndrom : Ursachen, Symptome, Behandlung
- Mg 34 Laufhülse Verriegelung : Laufhülse "TEC-HRO tube-Auflage"
- Meteo Île-De-France Par Météo-France
- Messe Vorschau: Finest Whisky Deluxe
- Miami Nach Atlanta Per Flugzeug, Zug, Bus Oder Auto