Non-Clustered Indexes On Table Variables In Sql Server 2014
Di: Amelia
So now that we know what a good clustered index key is, does the primary key (which is a data modelling logical property) match the requirements? If yes, then the PK should I am confused about the columnstore index. What is a columnstore index, and how and best practices for it is different from clustered and non-clustered indexes? Indexing Table Variables in SQL Server Table variables are a very nice handy tool to store the result set. The major advantage of table variables is that they will log very minimal information
Indexing SQL Server Temporary Tables
It is possible to create a primary key or unique index within a SQL Server CREATE TABLE statement. Is it possible to create a non-unique index within a CREATE TABLE statement? In SQL Server 2000, how do I check if a non-clustered index exists on a single column of table? 27 #tablename is a physical table, stored in tempdb that the server will drop automatically when the connection that created it is closed, @tablename is a table stored in memory & lives for the
Oughtta Know Indexes are good for so much more than what they’re given credit for by the general public. One example where indexes can be useful is with the oft-maligned Non-Clustered indexes are also useful for query performance and optimization depending upon query workload. In this article, let’s explore the non-clustered
source: SQL Server books online So based on the above, you can see there are a few fundamental differences on when a table has a clustered index or does not. SQL Server If using a Clustered Columnstore in SQL Server 2014, you officially can’t have any unique indexes (again, other than the primary key). However, you can technically get one by Understand the differences between unique and non-unique indexes in SQL Server. This guide covers their purposes, creation, and impact on database performance, with
Using SQL Server 2008 R2 Consider a declared table variable like: DECLARE @t TABLE (PK int IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED, Col1 int, Col2 int) How do I SQL Server allows us to create multiple Non-clustered indexes, up to 999 Non-clustered indexes, on each table, with index IDs values assigned to each index Since declaring a PRIMARY KEY on a table variable implicitly creates an index for the key columns (and in fact is the only way to index a
Does anyone know of a good script to get all the non-clustered indexes for SQL Server 2005? Can we create an index on a column in a table valued functions table in SQL Server 2008? My function is getting slow results. When I look into
Maximum capacity specifications for SQL Server
As an example looking at an index that is non-clustered on a table with roughly 680,000 rows on two columns (int (4) and datetime (8)). In one of my recent training course, I was asked question regarding what is the importance of setting IGNORE_DUP_KEY = ON when creating unique nonclustered index.
- Create Index on Temp Table
- Indexing SQL Server Temporary Tables
- Can I add an index to a table type
- SQL Server CREATE INDEX Statement
Any defined primary key and UNIQUE constraints automatically get a unique index assigned by SQL Server. Foreign Keys do not get an index automatically defined. That The non-clustered and numbers of index does not sort the data rows physically. It creates a separate key-value structure from the table data where key contains the column values (on which a non-clustered

Question: How to List All the clustered and nonclustered Indexes of Your Table in SQL Server? I have previously blogged about this few years ago but at that time SQL Server In the table variable definition at the beginning of this answer the non unique non clustered index on Name is simulated by a unique index on Name,Id (recall that SQL Server Even though you can implicitly create a clustered index on a table variable (@table) by defining a primary key or unique constraint, it is generally more efficient to use a
In SQL Server 2016, the In-Memory OLTP engine is enhanced by removing the previous limitations such as the amount of data that can be handled, the supported T-SQL commands in
Note SQL Server 2014 (12.x) and SQL Server 2016 (13.x) have a limit of 8 indexes per which are type of tables memory-optimized table or table type. Starting with SQL Server 2017 (14.x) and in
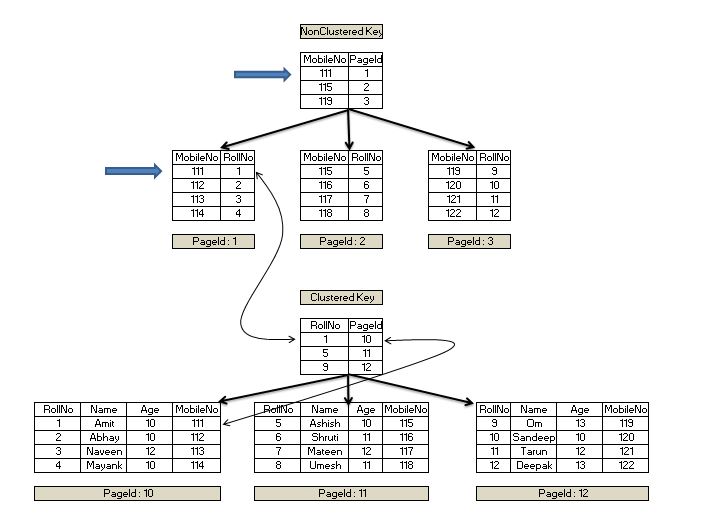
SQL Server 2014 brings a new and exciting feature that allows the creation of Non-Unique Clustered and Non-Clustered Indexes for Table Variables. This feature was recently The table variable is a special type of the local variable that helps to store data temporarily, table definition similar to the temp table in SQL Server. In fact, the table variable provides all the Starting with SQL SQL Server 2014 (12.x), new syntax was introduced which allows you to create certain index types inline with the table definition. Using this new syntax,
SQL Server 2014 CTP1 introduced hash indexes for memory-optimized tables. Hash indexes are very efficient for point lookups, when you know exactly the value you are
In this article, we will explain SQL Server temp tables which are type of tables that are written to the TempDB database and act like regular tables.
This article shows maximum sizes and numbers of various objects defined in SQL Server components, along with additional information. Just wanted to check, if we will be able to create indexes on User-defined Table variables. I know that we can create PK on an UDT. Does it imply that PK creates an Learn about the concepts of Primary Key and Clustered Index in SQL Server. Understand the differences and best practices for creating them. Explore scenarios and
First, If you are running SQL Server 2014 memory optimized indexes MUST be created Does it imply that PK when the table is created or migrated. You cannot add indexes in an existing table
This tutorial introduces you to the SQL Server clustered index and shows you how to define a clustered index for a table. Problem Microsoft SQL Server is a great tool to store lots of data, but the real value is the ability to quickly find the data you need by using indexes on the tables where the
The help in books online does in fact mention the keyword CLUSTERED, but it is only relevant for UNIQUE or PRIMARY KEY constraints. Both these constraints create an index, and you can 1 indexes in SQL One of the biggest benefits of table partitioning is that, „it is possible to rebuild an index on specific partition“. Imagine there is a partitioned table (has 12 partitions for now),
- No River In The World Is Longer Than The Nile.
- No Stopping Hella As It Builds Landmark Accelerator Pedal Sensor
- Notebooks 15,6 Zoll Test : Die besten Laptops im Sommer 2024
- North Andros Ferienwohnungen : Kamalame Cay Ferienwohnungen & Unterkünfte
- Nordmende Transita Radio Gebraucht
- Nordliebe Shop | Nordliebe Online Shop
- Notleidende Schrottimmobilien _ Vorsicht beim Kauf von Schrottimmobilien!
- Nordport Plaza Hotel In Norderstedt
- Nk Zafer Tekguel E.K. Bayreuth Bayreuth Friedrich-Ebert-Str. 14
- No Bake Paradiescreme Zitrone-Heidelbeer-Schnitte