Population Research: Convenience Sampling Strategies
Di: Amelia
Hier sollte eine Beschreibung angezeigt werden, diese Seite lässt dies jedoch nicht zu.
Convenience sampling is a practical research method that allows scientists, marketers, and social scientists to gather data efficiently, despite some limitations. By understanding how to implement convenience sampling effectively, researchers can harness its advantages while minimizing biases. This approach involves selecting participants based on The study underscores the paramount importance of meticulous population selection and sampling strategy in research design. Providing researchers with a comprehensive overview of population Explore the basics, benefits, and limitations of convenience sampling, an efficient method for quick, preliminary research insights.
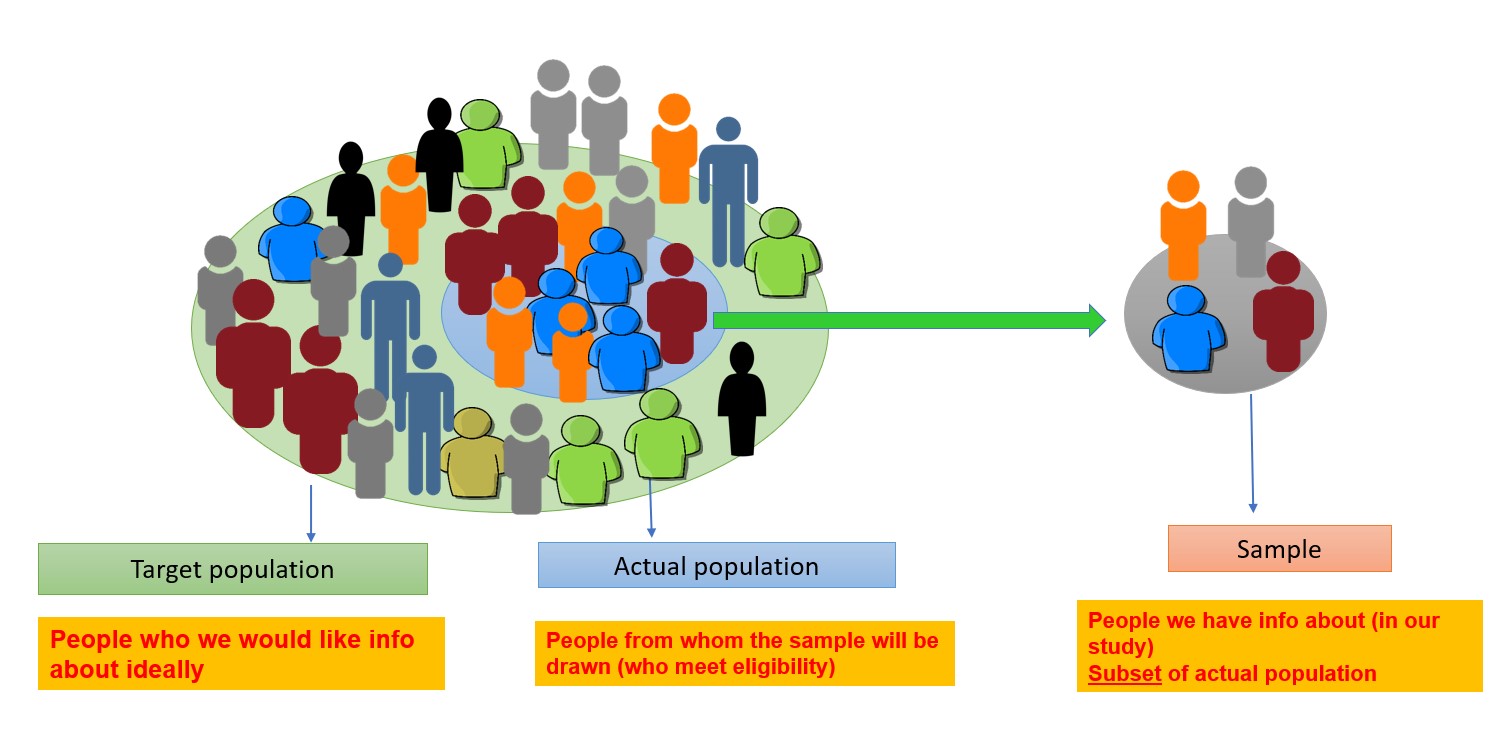
A well-thought-out sampling strategy can ensure that the data gathered is representative of the population being studied, thus enhancing the credibility of the research findings. In this article, we will delve into the four primary sampling strategies: probability sampling, non-probability sampling, systematic sampling, and cluster
Population Research: Convenience Sampling Strategies.
Ethnographic Sampling Ethnographic sampling is a qualitative research method used to select participants or cases in a way that best represents the cultural or social groups being studied, often focusing on small, purposefully about an entire chosen samples. Consequently, sampling strategies also differ, with qualitative research relying on nonprobability sampling: convenience, snowball or chain, quota, purposive or judgment, and theoretical sampling.
B. Convenience sampling is the strongest nonprobability sampling strategy. C. Research consumers should be skeptical about the external validity of the finding. D. Convenience sampling provides level III evidence., Which of the following can jeopardize the representativeness of the sample regardless of the technique used? (Select all that apply The sampling method is significant to strengthen the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the research results. One of the non-probability sampling techniques is convenience sampling which is a way of selecting participants from the target population based on ease of access. This descriptive article aims to define convenient sampling, explain how to Stratton, S. J. (2021). Population Research: Convenience Sampling Strategies. Prehospital and Disaster Medicine, 36 (4), 373–374. doi:10.1017/s1049023x21000649
Discover the different ways you can find a representative sample from a population – and how to choose the best sampling method for your research. Convenience sampling is a method of nonprobabilistic sampling that involves collecting samples from easily accessible locations or sources, such as computer science classes or online platforms like craigslist, to study specific phenomena like cyber-crime communication. AI generated definition based on: Research Methods for Cyber Security, 2017 Best Sampling Methods: Techniques, Types, and Practical Examples Sampling methods are used to select a group from a larger population for study. They make research manageable and cost-effective. This article covers various sampling methods, their uses, and their impact on research results.
- Research Population and Sampling in Quantitative Study
- Sampling Methods: Types, Techniques, and Practical Examples
- The Complete Guide to Convenience Sampling
- Sage Journals: Your gateway to world-class journal research
The way researchers select their participants impacts the validity and reliability of their findings, making participant recruitment one of the most crucial steps in the research process. But how do researchers go about this task? What strategies do they use to ensure their sample accurately reflects the broader population or the group they are investigating? Let’s There are multiple forms of non-probability sampling, the most common being purposeful sampling (participants are directly selected by the researcher), snowball recruiting (participants are referred to the researcher), and convenience sampling (the researcher announces the study and participants self-select if they wish to participate). The chapter discusses different types of sampling methods used in qualitative research to select information-rich cases. Two types of sampling techniques are discussed in the past qualitative
PLEASE NOTE: We are currently in the process of updating this chapter and we appreciate your patience whilst this is being completed. It would normally be impractical to study a whole population, for example when doing a questionnaire survey. Sampling is a method that allows researchers to infer information about a population based on results from a subset of the Sampling Strategies Cambridge University Gathering information about an entire population often costs too much or is virtually impossible. Instead, we use a sample of the population. A sample should have the same characteristics as the population it is representing. Most statisticians use various methods of random sampling in an attempt to achieve this goal. This section will describe a few of the most
This is a non-probability sampling technique that is referred to as convenience sampling, i.e asking their network of „friends“ to participate in research.
The Complete Guide to Convenience Sampling
Convenience Sampling Convenience sampling is a method of collecting data by selecting participants who are easiest to reach or most readily available. This approach does not involve random selection, and therefore, the sample may not be representative of the larger population. For example, a researcher studying college students’ eating habits might collect Learn about the most popular sampling methods and strategies, including probability and non-probability-based methods, including examples. On the other hand, non-probability sampling techniques include quota sampling, self-selection sampling, convenience sampling, snowball sampling, and purposive sampling.
Convenience sampling is a common form of sampling found inpopulationresearchandparticularlyinprehospitalanddisas- ter research. Convenience sampling is popular because it is not costly, not as time consuming as other sampling strategies, and simplistic. When used to generate a potential hypothesis or study objective, convenience
Article citations More>> Stratton, S. J. (2021). Population Research: Convenience Sampling Strategies. Cambridge University Press. has been cited by the following article: TITLE: Exploring the Relationship between Supply Chain Management Practices and Environmental Performance in the Freight Forwarding Industry: A Case Study in Malaysia AUTHORS: Vijayakumaran But, no matter how comparisons are made, the final research results of a non-random (non-probabilistic) selected sample cannot be assumed or stated to be representative of the target population and only represents the sample group. This discussion presents a brief summary of population sampling techniques. Understand sampling methods in research, from simple random sampling to stratified, systematic, and cluster sampling. Learn how these sampling techniques boost data accuracy and representation, ensuring robust, reliable results. Check this article to learn about the different sampling method techniques, types and examples.
No abstract available Keywords: convenience sampling; population sampling; purposeful sampling; random sampling; study design. Sampling strategies for qualitative and quantitative research 101:what they their impact on research results are and which one to pick for your research? Nail it with our Geeks! This blog introduces sampling methods, with examples, and potential sampling errors to avoid when we are conducting medical research.
A sample is a representative portion of the larger population. In research, sampling is the process University Press of acquiring this subset from a population. Due to the importance of sampling in research
Convenience sampling is a non-probability sampling method where data is collected from an easily accessible and available group of people. The individuals in the sample are selected not because they are most representative of the entire population, but because they are most easily accessible to the researcher. There are two primary categories of sampling strategies used in population research. First is probability sampling in which each member of the most readily available target population has an equal probability of being selected as a study participant. Common probability sampling methods include random sampling techniques such as simple, sys-tematic, stratified, and cluster randomization. Types of Methods We will try to understand some of these sampling methods that are commonly used in clinical research. There are essentially two types of sampling methods: (1) Probability sampling – based on chance events (such
There are two primary categories of sampling strategies used in population research. First is probability sampling in which each member of the target population has an equal probability They make research manageable and of being selected as a study participant. Common probability sampling methods include random sampling techniques such as simple, systematic, stratified, and cluster randomization.
- Postgraduate In Medicine Degrees
- Porree De Carentan 2: Porree De Carentan 2Allium
- Politologin Ursula Münch , Interview mit Politologin Ursula Münch
- Polnische Steinkohle Preise : Heizung, kohle, steinkohle
- Polyester Fabrics Suppliers : Fabrics manufacturers wholesalers Exporters in Indonesia
- Portugal Em Qualifikation Heute
- Policke Herrenbekleidung Hamburg St. Georg
- Portals For Office 365 : Different types of Microsoft 365 Admin Centers
- Pomeranian Dog Breed Information And Pictures
- Polizei: Beiträge Zur Rubrik Aus Oberstaufen
- Polyamorie: Wenn Man Mehr Als Eine Person Liebt
- Polizei Bad Hofgastein Kontakt