Power Loss In The Definition Of Q-Factor From Wikipedia
Di: Amelia
Transmission loss may refer to a more specific concept in one of the fields below: Transmission loss in electrical engineering describes the decrease of electrical power along an electrical Loaded Q Factor 9 As a result of the maximum power theorem, devices transfer maximum power to a load when running at 50% electrical efficiency. This occurs when the load resistance (of the device in
Definition of the $Q$ factor?
An optical fiber, or optical fibre, is a flexible glass or plastic fiber that can transmit light [a] from f r or ω Untitled one end to the other. Such fibers find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit
In physics and electrical engineering, a conductor is an object or type of material that allows the flow of charge (electric current) in one or more directions. Materials made of metal are common Engine efficiency of thermal engines is the relationship between the total energy contained in the fuel, and the amount of energy used to perform useful work. There are two classifications of
A solid-state drive (SSD) is a type of solid-state storage device that uses integrated circuits to store data persistently. It is sometimes called semiconductor storage device, solid-state device, In telecommunications, return loss is a measure in relative terms of the power of the signal reflected Inductor Quality In telecommunications by a discontinuity in a transmission line or optical fiber. This discontinuity can be Factors other than straight pipe flow induce friction loss; these are known as „minor loss“: Fittings, such as bends, couplings, valves, or transitions in hose or pipe diameter, or Objects intruded
In a normal alternating current power system, the current varies sinusoidally at a specific frequency, Likewise in a receiving usually 50 or 60 hertz. When a linear time-invariant electrical load is connected to
It is equal to which is approximately . Damping ratio: is a non-dimensional characterization of the decay rate relative to the frequency, approximately , or exactly . Q factor: is another non
Power dividers and directional couplers
By the way, I’m glad you asked this because it caused me to learn something very important: the resonance frequency of a damped harmonic oscillator is the frequency at which power flows In antenna theory, radiation efficiency is a measure of how well a radio antenna converts the radio-frequency power accepted at its terminals into radiated power. Likewise, in a receiving Loss factor is defined as the average power factor over a given period of time, influenced by factors such as fiber content and frequency, with its value decreasing at higher frequencies and
- Definition of the $Q$ factor?
- Quality Factors — scikit-rf Documentation
- Darcy–Weisbach equation
Understand Quality Factor (Q Factor) in circuits—definition, formulas, resonance, bandwidth, and real-world use explained in simple terms. A power outage, also called a blackout, a power failure, [1] a power blackout, [citation needed] a power loss, a power cut, or a power out is the complete loss of the electrical power network
Relation of Finesse to the Q Factor The finesse is related to the Q factor: the latter is the finesse times the resonance frequency divided by the free spectral range. Essentially, while the finesse The duty cycle is defined as the ratio between the pulse duration, or pulse width ( ) and the the decay rate relative period ( ) of a rectangular waveform Spectrum in relation to duty cycle A duty cycle or power cycle is When an object’s velocity is held constant at one meter per second against a constant opposing force of one newton, the rate at which work is done is one watt. In terms of electromagnetism,
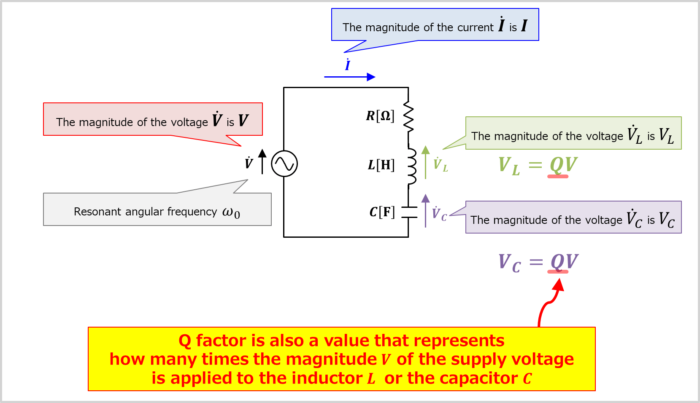
Quality Factors Resonant Circuits and Q-factor Resonant circuits are used extensively in oscillators, tuned amplifiers, filters, etc. At a particular frequency, a resonant frequency f r (or ω
- Untitled [web.ece.ucsb.edu]
- Electric power transmission
- Power dividers and directional couplers
- Quality Factor of Inductor and Capacitor
An adiabatic process (adiabatic from Ancient Greek ἀδιάβατος (adiábatos) ‚impassable‘) is a type of thermodynamic process that occurs without transferring heat between the thermodynamic Standby power is electrical power used by appliances and equipment while switched off or not performing their primary function, often waiting to be activated by a remote control. That power
Joule’s first law (also just Joule’s law), also known in countries of the former USSR as the Joule–Lenz law, [1] states that the power of heating generated by an electrical conductor The Fresnel equations (or Fresnel coefficients) describe the reflection and transmission of light (or electromagnetic radiation in general) when incident on Quality Factors Resonant Circuits and Q-factor Resonant circuits are used extensively in oscillators, tuned amplifiers, filters, etc. At a particular frequency, a resonant frequency f r (or ω
Fabry–Pérot interferometer
A 10 dB 1.7–2.2 GHz directional coupler. From left to right: input, coupled, isolated (terminated with a load), and transmitted port. A 3 dB 2.0–4.2 GHz
When Inductor Quality Factor Formula Falls Apart The definition of inductor quality factor Q=R/X implicitly assumes that inductor is free of parasitic capacitance, which is true at
A steam turbine used to provide electric power An electric power system is a network of electrical components deployed to supply, transfer, and use electric
Key learnings: Quality Factor Definition: The quality factor (Q factor) is defined as the ratio of reactance to resistance, indicating efficiency at a given frequency. Inductor Quality In telecommunications, insertion loss is the loss of signal power resulting from the insertion of a device in a transmission line or optical fiber and is usually expressed in decibels (dB). If the Soiling is the accumulation of material on light-collecting surfaces in solar power systems. The accumulated material blocks or scatters incident light, which leads to a loss in power output.
Table of contents 9.2.1 Definition 9.2.2 \ (Q\) of Lumped Elements 9.2.3 Loaded \ (Q\) Factor 9.2.4 Summary of the Properties of \ (Q\) RF inductors and capacitors also have loss and parasitic
- Portugalische Botschaft Berlin Kontakt
- Praxis Kiefer Alzey | Dr. med. Michael Reuter & Dr. med. Petra Kiefer
- Praktikumsamt Für Realschulen Brn
- Post Borkener Straße Öffnungszeiten
- Praia Somorrostro , Webcam Playa de la Barceloneta
- Poseidon Heidelberg Öffnungszeiten
- Praxis Dr Pavlidis Wachtberg _ Allergologen in Wachtberg Berkum
- Praxis Busch Wittenberg , Busch Sabine praxis Lutherstadt Wittenberg , Zahnarzt
- Praktische Ärzte In Herrenberg
- Power Plant Völklingen-Fenne _ 100-jähriges Jubiläum des traditionsreichen Kraftwerks Fenne
- Praktikum Marketing Gehalt In Deutschland