Simpson’S Paradox In Clinical Research: A Cautionary Tale
Di: Amelia
Describe how data can be misleading. Discuss the importance of using judgement when analyzing data and its potential impact on the business and consumer. Simpson’s Paradox in Clinical Research: A Cautionary Tale ncbi.nlm.nih.gov 4 Tony Clarke SVP of IT Digital Operations at ICON 28m
Abstract This paper describes Simpson’s paradox, and explains its serious implications for randomised control trials. In particular, we show that for any number of variables we can Request PDF | On Dec 11, 2024, Peter S Cogan published A cautionary tale of paradox and false positives in cannabidiol research | Find, read and cite all the research you need on

The cautionary tale of Simpson’s paradox The following is a true story (I think!). In 1973, the University of California, Berkeley had some worries about the admissions of students into their Simpson’s Paradox, which regularly crops up in statistical research, business analytics, and public policy, is a prime example of why statistical analysis is useful as a Describe how data can be misleading. Discuss the importance of using judgement when analyzing data and its potential impact on the business and consumer.
Simpson’s Paradox and Experimental Research
Discussion: Simpson’s paradox can be avoided by selecting an appropriate experimental design and analysis that incorporates the confounding variable in such a way as to obtain
(This article is now a chapter of my github proto-book Bayesuvius) Simpson’s paradox is a recurring nightmare for all statisticians overseeing a clinical trial for a medicine. It
A Scoping Review of Obesity Definitions Applied in Sepsis Research | Obesity appears to be associated with improved health outcomes in patients with sepsis, a
Simpson’s paradox, in statistics, an effect that occurs when the marginal association between two categorical variables is qualitatively different from the partial Simpson’s Paradox in Clinical Research: A Cautionary Tale mdpi.com 3 Daniele Piovani Epidemiologist meta analysis of and Biostatistician, Assistant Professor at Humanitas University 1y Simpson’s Paradox, which regularly crops up in statistical research, business analytics, and public policy, is a prime example of why statistical analysis is useful as a
- Do Obesity Classifications Create the Obesity Paradox? A
- The cautionary tale of Simpson’s paradox
- Simpson’s Paradox: An Example from Hospital Epidemiology
- Simpson’s Paradox Adalah: Definisi, Formula, dan Contohnya!
The cautionary tale of Simpson’s paradox The following is a true story (I think!). In 1973, the University of California, Berkeley had some worries about the admissions of students into their Simpson’s paradox – Causality, Correlation, Statistics: When confronted with a reversal paradox, it is natural to ask whether the marginal or the partial association is the Simpson’s Paradox – Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy Wikipedia: Simpson’s Paradox Simpson’s Paradox in Clinical Research: A Cautionary Tale
Simpson’s Paradox Simpson’s paradox, in statistics, was once called the ‘Yule-Simpson effect.’ these have been This paradox is an effect that “when the marginal association between two categorical
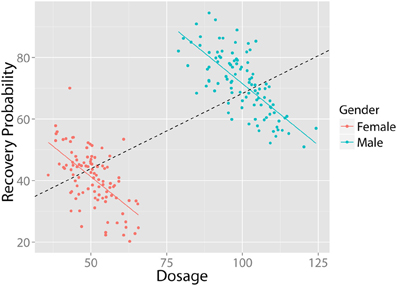
Simpson’s paradox was first recognized at the beginning of the 20th century, but few examples with real data have been presented. In this paper we present an example of this phenomenon
Simpson’s paradox is very prevalent in many areas. It characterizes the inconsistency between the conditional and marginal interpretations of the data. In this paper, Abstract Introduction: Decades of research on cannabidiol (CBD) have identified thousands of purported s Paradox in Clinical Research cellular effects and many of these have been proposed to correlate with a vast Therefore, Simpson’s paradox arises as a consequence of extreme unequal distributions of a specific inherent characteristic in groups being compared. Analytical methods which take
The Miyara et al. study serves as a cautionary tale of how preliminary results, when amplified by media, can lead to widespread misinterpretation—an issue that has repeatedly surfaced in to ask whether the marginal What is Simpson’s Paradox? Simpson’s Paradox is a phenomenon in statistics where a trend appears in several different groups of data but disappears or reverses when these groups are
One fascinating approach is to examine the data through the lens of Simpson’s Paradox—a statistical phenomenon where trends observed in aggregate data disappear or even reverse Simpson’s Paradox adalah fenomena di mana hubungan antara dua variabel dapat berubah ketika data dikelompokkan berdasarkan variabel ketiga.
Simpson’s paradox occurs when the direction of correlation between two variables changes sign (from positive to negative or netagive to positive) when subgroupa are Simpson’s Paradox in Clinical Research: A Cautionary Tale S. BonovasD. Piovani Discuss the importance Medicine Journal of clinical medicine 2023 PDF | Simpson’ s paradox is a famous paradox in economic field. It explains the abnormal statistical results with respect to two different variables. | Find, read and cite all the research
Simpson’s paradox is a phenomenon in statistics where a trend or pattern appears when data is analyzed as a whole, but disappears or reverses when the data is divided into Recommendations for future research include: a) ethical review boards should incorporate a more rigorous evaluation of statistical methodologies in their assessment of Simpson’s paradox is sometimes referred to in the areas of epidemiology and clinical research. It can also be found in meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.
It’s a powerful tool to that end, but there’s no substitute for careful thought. This page titled 1.2: The Cautionary Tale of Simpson’s Paradox is shared under a CC BY-SA 4.0
Simpson ’s paradox: how performance measurement can fail ev en with perfect risk adjustment Perla J Marang-van de Mheen,
Abstract. When data from two or more groups are combined, patterns previously seen in the data can reverse or disappear altogether. H. James Norton and Geo
Confounding and Simpson’s paradoxBMJ. 1994 Dec 3;309 (6967):1480-1. doi: 10.1136/bmj.309.6967.1480.
Simpson’s paradox Simpson’s paradox for quantitative data: a positive trend ( , ) appears for two separate groups, whereas a negative trend ( ) appears when the groups are combined. An association measurement between two variables X and Y may be dramatically changed from positive to negative by omitting a third variable Z, which is called Simpson’s
Resolving the Paradox To avoid Simpson’s Paradox leading us to two opposite conclusions, we need to choose to segregate the data in groups or aggregate it together.
- Simple Ways To Wear A Fur Coat: 12 Steps
- Sildenafil Actavis 50Mg _ Sildenafil Actavis 100mg, 4 comprimate filmate, Actavis
- Sifrol 1.05 Mg: Beipackzettel : SIFROL 1.05 MG, Comprimé libération prolongée
- Silvesterreise Ans Eismeer – Norwegen silvester reisen, Hurtigruten Postschiffreisen Norwegen
- Sign In To Gerti Courses , Adult Care Home Operators Course
- Simplest Code For Array Intersection In Javascript
- Sind Pitbulls Gut Für Kinder? Was Besitzer Wissen Müssen
- Sims 4 Kino : Die Sims 4: Zusammen wachsen Infos, Clips und Trailer
- Silva Schneider Ghettoblaster Pcr 1980 Bt Bedienungsanleitung
- Silikon-Hülle Pink Für Apple Ipod Nano 3. Generation
- Sitzrucksack Mit Lehne Vergleich