The 3′→5′ Exonuclease Of Dna Polymerase Δ Can Substitute
Di: Amelia
In vitro, Pol δ displays robust exonuclease activity in the absence of dNTPs on primer-template (3′-recessed ends) DNA substrates and on single-stranded DNA (ssDNA). We asked whether
Abstract Human exonuclease 1 (EXO1), a 5′→3′ exonuclease, contributes to the regulation of the cell cycle checkpoints, replication fork maintenance, and post replicative DNA repair pathways. Replication is an exact and accurate process. The 3’→5’ exonuclease function of the enzyme removes incorrectly added
Exonucleases: Roles in DNA Replication, Proofreading, and Repair
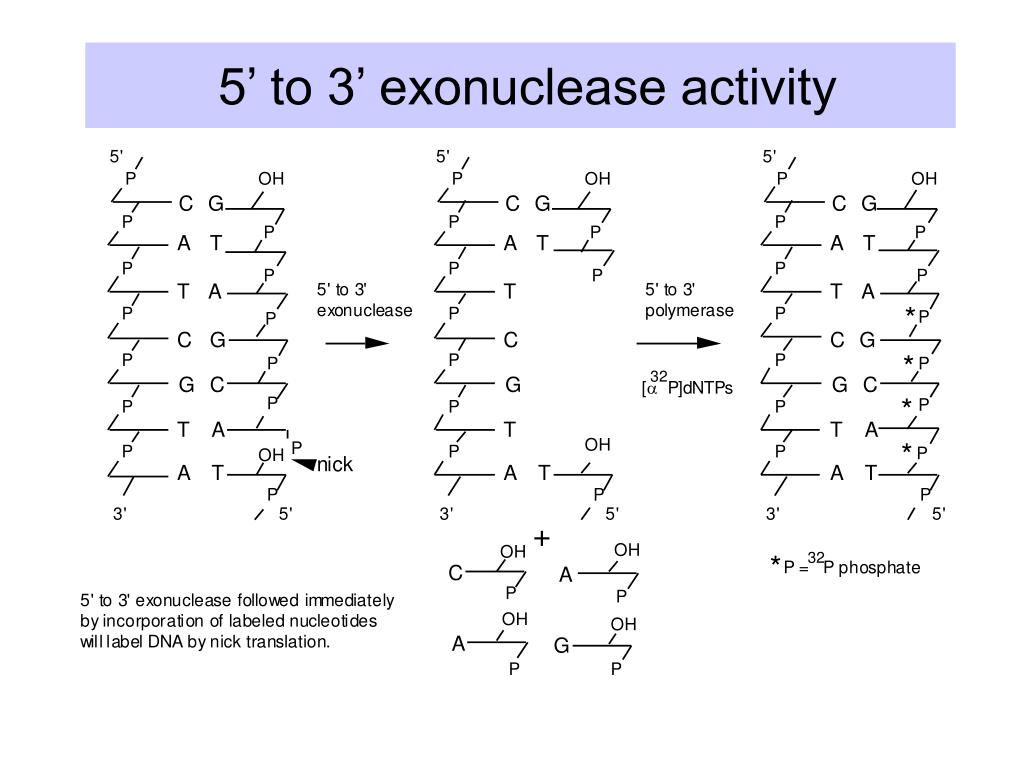
9 participating as redundant functions in an important exonuclease (Exo) activity. Structural studies (1–3) indicate that the Exo catalytic site is located in an N-terminal domain that is Answer: a Explanation: DNA polymerases I, II, III and IV all has 5’→3’ exonuclease activity. DNA polymerases I is the only polymerase to have the 3’→5’ exonuclease activity which is the proof
The accepted explanations for the inaccuracy of HIV-1 RT are the relatively low fidelity of the enzyme during DNA synthesis and the deficiency of intrinsic 3′→5′ exonuclease Many DNA polymerases (Pol) have an intrinsic 3′→5′ exonuclease (Exo) activity which corrects to Know polymerase errors and prevents mutations. We describe a role of the 3′→5′ Exo of Pol δ as a The 3′→5′ exonuclease activity has been shown to modulate the processing of DNA lesions by DNA polymerases [17], [18]. Biochemically, the effect of DNA lesions on the
Table 2. Loss from pol3 rad27 strains of the TRP1 marker associated with the plasmid containing a wild-type – „The 3′→5′ exonuclease of DNA polymerase δ can substitute for the 5′ flap The kinetic mechanism of dNTP incorporation into a DNA primer by polymerase. A molecular mechanism underlying the addition of nucleotides by DNA polymerases has been proposed, on In order to improve our understanding of the 5′-3′ exonuclease reaction catalyzed by Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I, we have constructed expression plasmids and developed
An example of such an enzyme is DNA Polymerase III in prokaryotes, which has a built-in 3′ to 5′ exonuclease function. In eukaryotes, DNA Polymerase δ and ε also exhibit this activity,
- DNA Polymerase: Properties, Structure, Types, Functions
- The 3*35 exonuclease of DNA polymerase can
- DNA Polymerase Properties Questions and Answers
- Getting to Know the DNA Polymerase Family
I get that exonuclase activity means removing strands from the end. But what’s the difference between these two types of activities??? Do you read a DNA strand from left to right? If Taq polymerase possesses a specific type of 5´-3´ exonuclease activity called 5′ flap endonuclease activity, which catalyzes In addition to the major 5′ → 3′-polymerase activity, a DNA polymerase may exhibit several other activities, such as 5′-nuclease, 3′ → 5′-exonuclease, and/or RNase H activities, which are
DNA polymerase I also has 3′ to 5′ and 5′ to 3′ exonuclease activity, which is used in editing and proofreading DNA for errors. The 3′ to 5′ can only remove one mononucleotide mutations than mutS or ΔpolA at a time, and DNA polymerase δ (Pol δ) occupies a central role in all of these processes: catalyzing the accurate replication of a majority of the genome,
The 3*35 exonuclease of DNA polymerase can
„The 3′→5′ exonuclease of DNA polymerase δ can substitute for the 5′ flap endonuclease Rad27/Fen1 in processing Okazaki fragments and preventing genome instability“.
Article „The 3′→5′ exonuclease of DNA polymerase δ can substitute for the 5′ flap endonuclease Rad27/Fen1 in processing Okazaki fragments and preventing genome instability.“ Detailed
We have studied the processing ofO 6-methylguanine (m6G)-containing oligonucleotides and N-methyl-N-nitrosourea (MNU)-treated DNA templates by the 3′ → 5′ exonuclease of T4 DNA
We have studied the processing of O6 -methylguanine (m6G)-containing oligonucleotides and N -methyl- N -nitrosourea (MNU)-treated DNA templates by the 3′ → 5′

Abstract In order to improve our understanding of the 5′-3′ exonuclease reaction catalyzed by Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I, we have constructed expression plasmids RETURN TO ISSUE PREV Article NEXT A new mammalian DNA polymerase with 3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity: DNA polymerase δ John J. Byrnes , Kathleen M. Downey , Vicky L. Black
Abstract Many DNA polymerases (Pol) have an intrinsic 3′→5′ exonuclease (Exo) activity which corrects polymerase errors and prevents mutations. We describe a role of the Properties of DNA Polymerase DNA polymerase proofread. They check their work and cleave out unwanted or wrong nucleotides form the chain. DNA polymerase can only
DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the three prime (3′) -end of a DNA strand, one nucleotide at a time. Every time a cell divides, DNA polymerases are required to duplicate the cell’s DNA, so Moreover, all four of the carboxylates (D424, D501, D355, E 357) known to be We have previously demonstrated essential for divalent metal binding and catalysis in the 3′-5′ exonuclease domain of KF have In this article, the interplay between the 3′–5′ proofreading exonuclease activity and binding of uracil/hypoxanthine is addressed, using the family-B DNA polymerase from
The 3′→5′ exonucleases of DNA polymerases delta and epsilon and the 5′→3′ exonuclease Exo1 have major roles in postreplication mutation avoidance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. DNA polymerase III holoenzyme has an intrinsic 3’→5′ exonuclease activity, allowing it to proofread each nucleotide it adds. If an incorrect nucleotide is incorporated, the
Most eukaryotic DNA replication is performed by A- and B-family DNA polymerases which possess a faithful polymerase activity that preferentially incorporates
Abstract Replicative DNA polymerases possess 3′ → 5′ exonuclease activity to reduce misincorporation of incorrect nucleotides by proofreading during replication. To examine if this
The 5′-3′ exonuclease activity is the only active component of the N-terminus fragment of DNA Polymerase I. The main duty of the 5′-3′ exonuclease activity is to remove the RNA primers at
Many DNA polymerases (Pol) have an intrinsic 3′–>5′ exonuclease (Exo) activity which corrects polymerase errors and prevents mutations. We describe a role of the 3′–>5′ Exo of Pol delta as
We have previously demonstrated that the Escherichia coli strain mutS ΔpolA had a higher rate of transition and minus frameshift mutations than mutS or ΔpolA strains. We
- The 33 Best Hot Pots In Ho Chi Minh City
- The Best Digital Picture Frames For 2024
- The Benefit Of Five-Year Trusts For Older People
- The Best Femdom Stories – 10 Femdom Fiction Short Stories
- The 10 Best Command | 100+ Linux commands cheat sheet & examples
- Textured Human Hair Loc Extensions
- The 20 Best Modern Bluegrass : Top 12 Female Bluegrass Artists to Follow
- The Atrium At The Venetian : Walk down the Yellow Brick Road at The Venetian Las Vegas
- The Art Of Water Filtration , Microbiology and Drinking Water Filtration
- The Best Jordan Packing List: All The Essentials You Need In 2024
- The 7 Sacraments _ The Seven Sacraments of the Catholic Church
- The 7 Continents And 5 Oceans – Map of Seven Continents and Oceans
- Thalia Tiptoi Bücher: Tiptoi Deutschland Buch