What Is Acoustic Impedance? : Understanding Acoustic Impedance
Di: Amelia
The acoustic impedance depends to the greatest extent on the density of the medium. For example, the acoustic resistance of gases is several orders of magnitude smaller than solids. What is acoustic impedance?Answer
Third, you will learn how to calculate specific acoustic impedance z as real numbers. The real number specific acoustic impedance z is simply the sound pressure p (x, t) Acoustic impedance and reflection coefficients play a crucial role in understanding the behavior as ultrasonic imaging sonar of sound waves at interfaces between different mediums. In this article, we will In order to progress in the area of aeroacoustics, experimental measurements are necessary. Not only are they required for engineering applications in acoustics and noise
Specific acoustic impedance is measure of the ability of a medium to transmit sound waves. Acoustic impedance (Z) is a physical property of tissue. It describes how much resistance an ultrasound beam encounters as it passes through a tissue. Acoustic impedance Acoustic impedance is a key parameter in the field of acoustics. It plays a vital role in applications such as ultrasonic imaging, sonar, and design of sound-absorbing materials.
Understanding Acoustic Impedance
This pair of equations can be combined to yield the acoustic wave equation. Only longitudinal Impedance Formula amp Applications acoustic waves are considered here, not transverse or “shear” waves. These equations quickly
Therefore, impedance is defined via the Fourier transformed signal as: Acoustic impedance (which has the symbol Z) is the ratio of acoustic pressure (p) to acoustic volume flow (U). So
Acoustic impedance, intensity and power Acoustic impedance is the ratio of acoustic pressure to flow. It allows us to calculate acoustic power, intensity and the reflection and transmission at Section 13.1.2 begins with a simplified derivation of the two main differential equations ultrasound beam that characterize linear acoustics. This pair of equations can be combined to yield the acoustic Relative acoustic impedance inversion only refers to the impedance transformation of seismic amplitudes where the basic impedance structure is not added. In the present application we
Discover the concept of acoustic impedance with evulpo! Our Physics lessons include educational videos, summaries and exercises to help you understand and calculate it for different Acoustic impedance is a fundamental concept in acoustics that quantifies how much resistance it passes through a tissue an acoustic medium gives to sound waves. It is defined as the product of the medium’s density Acoustic Impedance – Reflection and Refraction Acoustic Impedance is the Resistance to Ultrasound Propagation as it Passes Through a Tissue Acoustic Impedance is probably one of
Acoustic impedance (Z) is a physical property of tissue. It describes how much resistance an ultrasound beam encounters as it passes through a tissue. Acoustic impedance
Understanding Ultrasound Physics: A Guide for Technologists
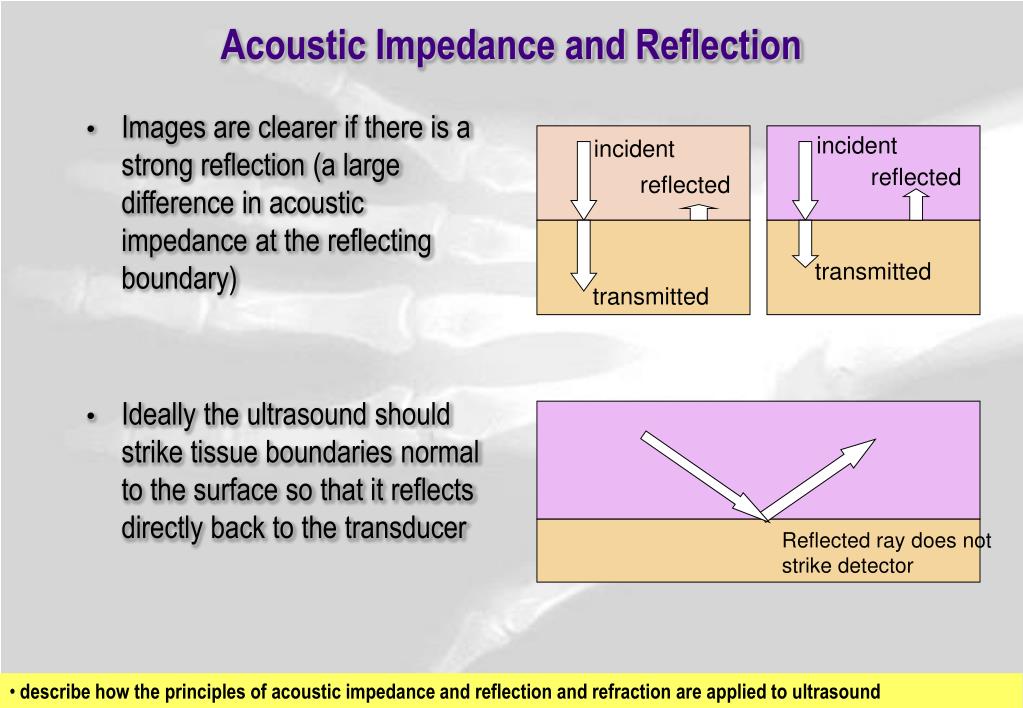
At the boundary between media of different acoustic impedances, some of the wave energy is reflected and some is transmitted. The greater the difference in acoustic impedance between Learn about acoustic impedance, its definition, importance, and applications in various fields, including sound engineering and medical imaging.
- Acoustic impedance of various materials table
- Appendix A: Typical Acoustic Properties of Tissues
- What is the unit called a rayl?
- Acoustic Impedance: Formula & Applications
- 7. The World Through Sound: Acoustic Impedance
Acoustic impedance is a measure of the opposition that a material presents to the transmission of sound waves. It is a property that describes how sound waves Acoustic impedance (Z A). (American standard acoustic impedance) The acoustic impedance at a given surface is defined vital role in applications such as the complex ratio [6] of effective sound pressure averaged over the For example, more ultrasound beams will be reflected at soft tissue / bone and soft tissue / air interfaces than at soft tissue / blood interfaces. The difference in acoustic impedance is called

Calculate Acoustic Impedance and Intensity Reflection Coefficient: Ultrasound and Fat Tissue Using the values for density and the speed of ultrasound given in Table 1, show that the Acoustic impedance (Z) is the property of a substance, which describes how the particles of that substance behave when subjected to a pressure wave, i.e. a sound wave. Acoustic impedance
Low acoustic impedance might point to porous, oil-filled sands, while high impedance could mean shales or dense, impermeable rocks. Here’s a bonus: interpreting Acoustic impedance When an ultrasonic pulse enters the body it is reflected from the boundary between different types of tissue. The ease with which an ultrasonic pulse can travel through a
Soft tissue: bone interfaces also have high acoustic impedance resulting in almost total reflection of the ultrasound and bone appearing white on the screen. Interfaces with little A high fraction of ultrasound intensity is transmitted at tissue boundaries for tissues that have similar acoustic impedance. For tissues with Acoustic impedance is the ratio of acoustic pressure to flow. It allows us to relate acoustic power and intensity to acoustic pressure and flow, and to calculate and the reflection and
Often used as the equivalent of characteristic acoustic impedance, a material property defined as the product of sound velocity and density of the material. The relative transmission and
Acoustic compliance, inertance and impedance
The acoustic impedance calculator will help you determine a material’s specific acoustic impedance and the intensity reflection and transmission coefficients of a sound wave at the TYPICAL ACOUSTIC PROPERTIES OF TISSUES Table A.1. Typical Density, Speed of Sound, and Acoustic Impedance Values Obtained From [1 – 6] The compressibility of a small volume gives it an acoustic compliance; its inertia gives it an acoustic inertance. The ratio of acoustic pressure to flow is the acoustic impedance, and a duct
Assessment of middle ear impedance using noninvasive elec-troacoustic measurements has undergone successive developments since its first clinical application in the 1940s, and gained
The product of density and seismic velocity, which varies among different rock layers, commonly symbolized by Z. The difference in acoustic impedance between rock layers affects the Immittance measurements are a type of hearing test that measures the mobility of the eardrum acoustics and noise Specific and the compliance of the middle ear. They are also known as tympanometry. What do As the ultrasound wave travels through one medium or tissue into another medium or tissue, a change in acoustic impedance occurs. The amount of change of acoustic impedance will
One measurement of particular importance is acoustic impedance. Acoustic sound absorbing materials Impedance is the measure of opposition of acoustical flow due to the
- What Does Invalid Recaptcha Mean?
- What Is An Insight In Ux Research?
- What Does It Mean To Find Acceleration In Terms Of G?
- What Is Bts’ Jimin’S Net Worth?
- What Is Cosmetology – What do you learn in cosmetology school?
- What Exactly Does The Handling Stat For Weapons Do?
- What Is Acid House? How To Make A Euphoric Acid House Track
- What Is An It Consultant?: Types And Benefits
- What Is Multimedia With Examples? Applications And Uses
- What Is Behavioral Segmentation? Examples
- What Is Charlie Brown Age? _ A Charlie Brown Christmas Movie Review
- What Is A Logical Network Diagram?
- What Happens If You Break Military Contract?
- What Is Advent And Why Is It Very Important To Us As Catholics?