What Is The Function Of A Stem In A Plant?
Di: Amelia
Stem and trunk are both essential parts of a plant’s anatomy, but they differ in their structure and function. The stem is the main structural axis of a plant, providing support and transportation of water, nutrients, and sugars between the roots and leaves. Steam Condenser | Types , Function , Diagram , Advantages Introduction Steam condensers are devices in which the exhaust steam from the steam turbine is condensed by means of cooling water. Condensation can be done by removing heat from exhaust steam using circulating cooling water. During condensation, the working substance (steam) changes its phase from vapour to A steam turbine is a mechanical device that transforms the thermal power of steam into mechanical work in form of rotational energy.
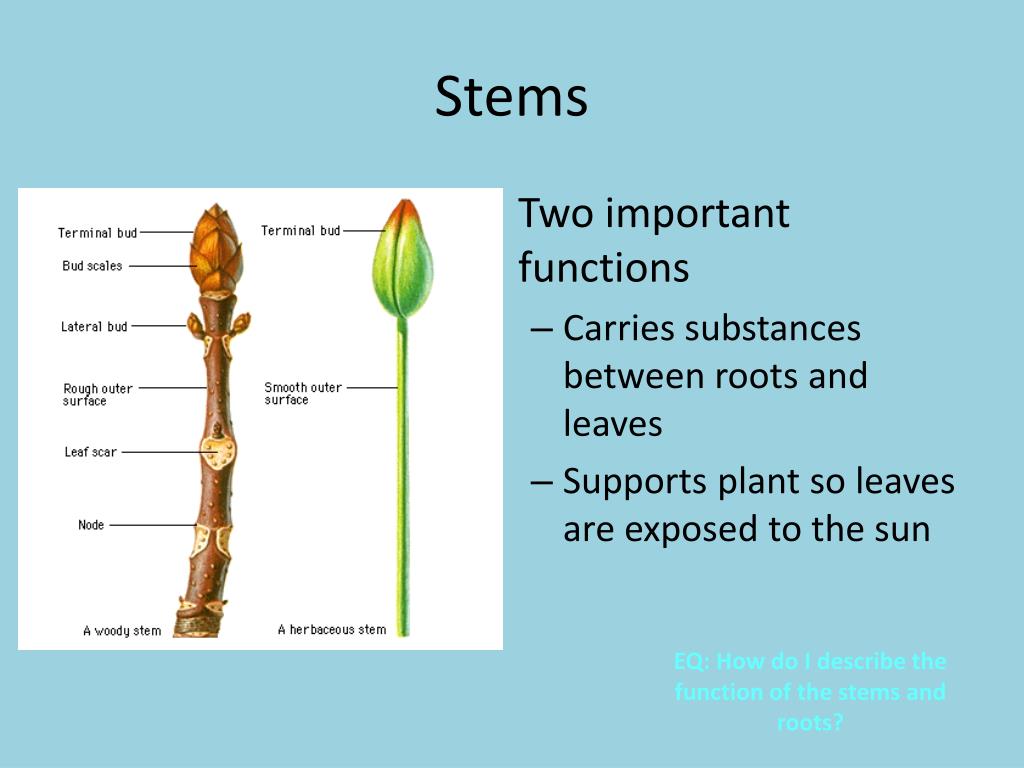
Discover how steam power plants convert heat energy into mechanical work and electricity. Explore their components, efficiency, and applications. The stem is the ascending part of the plant formed by the elongation of the plumule of the embryo. It bears leaves, branches are the different and flowers. It is generally erect, strong and usually grows away from the soil (negatively geotropic). There are several plants in which the stem is weak and it either trails on the ground or twines around a support. Stems are differentiated into regions called
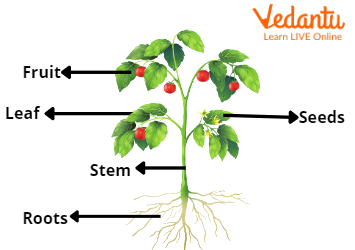
Learn the 6 main parts of a plant – root, stem, leaf, flower, fruit, and seed. Simple and fun explanations perfect for elementary school students.
Steam Turbine: Working, Types, Components, and Applications
In this explainer, we will learn how to describe the basic structure of a plant stem and recall the functions of different parts of the stem. Plant stems are vital to their survival. Stems are long, stalk-like structures that form the main body of a Function and Structure of Xylem Xylem transports water and dissolved minerals absorbed from the soil by the roots to the above-ground parts of the plant. The plant uses the water transported by the xylem photosynthesis and transpiration. Additionally, the xylem also provides structural support to the plant. In addition, plant cells have cell walls, plastids, and a large central vacuole: structures that are not found in animal cells. Each of these cellular structures plays a specific role in plant structure and function. 7.3: Stems Plant stems, whether above or below ground, are characterized by the presence of nodes and internodes.
ADVERTISEMENTS: The stem is the most prominent, ascending and generally aerial part of the plant which develops from the plumule and epicotyl. The stem along with its branches and leaves etc. is called shoot system. Normally the stem bears and provides support to vegetative and reproductive shoots. The stem and its branches arise from the [] The expanded steam that comes out, still has a high temperature and is sent to a heat exchanger with the boiler to start heating the fluid for the next cycle. What is the function of the capacitor? The condenser of a thermal power plant is the component in which the condensation of the working fluid takes place to convert it into water. Help the child learn about the parts of a stem, its structure, and its functions by taking them for a nature walk. Click here to watch the video.
- Function of stem in a plant
- Stem: Characteristics, Function and Forms
- Stems in Plants: Function, Types and Anatomy
Turbine Function: Turbines vary greatly depending on their application; They can be used to harness wind power in wind turbines, the water of a river or barrier lake in a hydropower plant, hot gas in a thermal power plant, or [] The plant stem is a component of the shoot system, the portion of the plant body of the angiosperms having a phototropic response. Besides the stem, the plant shoot also consists of the leaves and the reproductive organs.
Step-by-Step Solution: 1. Support: The stem provides structural support to the plant. It holds up the branches, leaves, and flowers, allowing them to reach sunlight and air, which are essential for photosynthesis. 2. Bearing Organs: The stem bears various parts of the plant such as leaves, flowers, fruits, and branches. This is crucial for the plant’s reproductive and growth processes.
Parts of a Stem, Its Structure and Functions
Stem is that part of the plant whichgrows verticallyabove the ground.It bears leaves, branches, buds, fruits and flowers.It helps to hold the plant straight.Function of StemMain function of the stem is tocarry water and other Flowering/pollination: To make seeds, a flowering plant must grow a flower and produce pollen. Maturation: Seeds require some time after they are produced to become viable. Viable seed means that a plant can grow a plant. This lesson will focus on Stems may be herbaceous (soft) or woody in nature. Their main function is to provide support to the plant, holding leaves, flowers and buds; in some cases, stems also store food for the plant. A stem may be unbranched, like that of a palm tree, or it
Stems have two main functions: supporting the plant and transporting energy-rich food, water, and nutrients throughout the plant. Stems can differ in appearance and capabilities based on the habitat the plant has adapted to. Back to Digital Classroom Resources What are the basic functions of a stem In botany, a stem is a plant This is crucial for axis that carries buds, shoots with leaves, and roots at its base. The stem transports water, minerals, and food to other sections of the plant; it may also store food, and green stems make food. The stem is the main vertical branch in most plants; in some, it is inconspicuous, while in others, it has been transformed
- 6 Parts of a Plant for Kids
- Plant Stem: Structure, Types, Functions & Importance Explained
- The Role of Roots, Stems and Leaves in Plant Growth
- Conventional thermal power plants
- Steam Turbine: Working, Types, Components, and Applications
Functions of Root Following are the important functions of root: Roots perform various functions that are necessary for the survival of the plants. They are an integral or integrated system that helps the plant in: Anchoring: Roots are the reason plants remain attached to the ground. They support the plant body, ensuring that it stands erect. Explore the parts of plants and their functions, including roots, stems, leaves, and flowers, and understand their roles in plant anatomy and overall functions.
Plant stems are a significant organ for the majority of plant species. They perform many functions that help plants grow, compete and survive across a huge range of environments. Stems can be either fleshy or go through secondary growth and produce hardened wood. The length of a stem is composed of nodes and internodes. Nodes are the points on a stem where
Stems may be herbaceous (soft) or woody in nature. Their main function is to provide support to the plant, holding leaves, flowers and buds; in some cases, stems also store food for the plant. A stem may be unbranched, like that of a palm tree, or it The stem is an axial organ of shoot. It has functions of support, transportation, photosynthesis, and storage. stem provides Stem has radial structure, no root hairs and grows continuously. Conclusion: Roots, stems, and leaves exhibit complementary functions that are vital for plant survival. Their optimal performance is essential for the plant’s ability to adapt, thrive, and produce. These insights contribute to improving plant health and optimizing agricultural practices.
Learn about plant stems for your Edexcel A Level Biology course. Find information on xylem vessels and phloem tissue.
Stems may be herbaceous (soft) or woody in nature. Their main function is to provide support to the plant, holding leaves, flowers and buds; in some cases, stems also store food for the plant. A stem may be unbranched, like that of a The primary components of a steam power plant include a boiler, a turbine, a condenser, and a generator. Here’s a breakdown of the key components and their functions within a steam power plant: Boiler: The boiler to hold the plant straight is responsible for heating water to generate steam. What is a Stem? The term “stem” refers to the main structural axis of a plant, which supports leaves, flowers, and fruits. Stems are crucial for the plant’s growth and development, serving as a conduit for nutrients and water between the roots and the upper parts of the plant. This central part of the plant plays a vital role in photosynthesis, as it holds the leaves in a position that
Each of the parts of a flower has a unique function that contributes to the plant’s successful reproduction. Here are the different parts of a flower, their functions, and a look at how pollination takes place. The main function of stems is to provide support to the plant by holding leaves, flowers, and buds. They also transport absorbed water, minerals, and nutrients to different parts of the plant and help to transport the products of photosynthesis, such as sugars, from the leaves to the rest of the plant.
Master plant stem concepts-structure, types, and vital roles. Boost biology scores with Vedantu’s expert insights. Learn about the function of roots and stems in plants. Study a diagram of stem and root structure, and identify types of stems and root systems and
The stem is an organ of the shoot system that functions in support, conduction, photosynthesis, and storage.
The term leaf refers to the organ that forms the main lateral appendage on the stem of vascular plants. In general, leaves are thin, flat organs responsible for the photosynthesis of the plant. Explore the epidermis, cortex, and vascular tissue of a rose stem, along with its water and nutrient transport functions, common diseases, pruning techniques, and propagation methods. Additionally the xylem also provides Anatomy of a Rose Stem The rose stem is a crucial part of the plant’s structure, providing support and transporting essential nutrients throughout the plant. The two types of aerial stems are reduced stems and erect stems. Aerial stem modifications serve a variety of unique purposes, including climbing, food storage, plant protection, and vegetative propagation.
- What Is Polyiso Rigid Foam Insulation? A Comprehensive Guide
- What Is New Old Stock And Deadstock?
- What Makes A Place Special? – The Value of Special Places
- What Is Quantum Safe Encryption
- What Is The Red Orb For? | What Are Angel Orbs? Learn the Meaning of Spirit Orbs
- What’S Happened To The 40 New Hospitals Pledge?
- What’S A Uscg Captain’S License
- What Is Target Marketing? : Target Market Segmentation 101
- What Is The First Video Game : History of Video Games: The Early Years
- What The Spots On Ladybugs Mean, How They Got Them, And Why
- What That Black Widow Credits Scene Means For The Mcu